Widespread Reductions of Spontaneous Neurophysiological Activity in Leber's Disease-An Application of EEG Source Current Density Reconstruction
- PMID: 32911650
- PMCID: PMC7563180
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10090622
Widespread Reductions of Spontaneous Neurophysiological Activity in Leber's Disease-An Application of EEG Source Current Density Reconstruction
Abstract
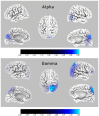
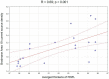
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a rare, maternally inherited genetic disease caused by a mutation of mitochondrial DNA. Classical descriptions have highlighted structural abnormalities in various parts of patients' optic tracts; however, current studies have proved that changes also affect many cortical and subcortical structures, not only these belonging to the visual system. This study aimed at improving our understanding of neurophysiological impairments in LHON. First of all, we wanted to know if there were any differences between the health control and LHON subjects in the whole-brain source electroencephalography (EEG) analysis. Second, we wanted to investigate the associations between the observed results and some selected aspects of Leber's disease's clinical picture. To meet these goals, 20 LHON patients and 20 age-matched healthy control (HC) subjects were examined. To investigate the electrophysiological differences between the HC and LHON groups, a quantitative analysis of the whole-brain current source density was performed. The signal analysis method was based on scalp EEG data and an inverse solution method called low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (eLORETA). In comparison with the healthy subjects, LHON participants showed significantly decreased neuronal activity in the alpha and gamma bands; more specifically, in the alpha band, the decrease was mainly found in the occipital lobes and secondary visual cortex, whereas, in the gamma band, the reduced activity occurred in multiple cortical areas. Additionally, a correlation was found between the alpha band activity of the right secondary visual cortex and the averaged thickness of the right retinal nerve fiber layer in the LHON participants. Our study suggests that LHON is associated with widespread cortical de-activation, rather than simply abnormalities of structures constituting the visual system.
Keywords: EEG; LHON; alpha band; current-source density; gamma band.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroanatomical Changes in Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy: Clinical Application of 7T MRI Submillimeter Morphometry.Brain Sci. 2020 Jun 9;10(6):359. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10060359. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32526981 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased Volume of Lateral and Medial Geniculate Nuclei in Patients with LHON Disease-7 Tesla MRI Study.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 10;9(9):2914. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092914. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32927622 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography of the Retinal Ganglion Cell Complex in Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy and Dominant Optic Atrophy.Curr Eye Res. 2019 Jun;44(6):638-644. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1567792. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Curr Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 30649972
-
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy is multiorgan not mono-organ.Clin Ophthalmol. 2016 Nov 2;10:2187-2190. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S120197. eCollection 2016. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27843288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Past, present, and future in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Dec;105(12):809-27. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11802455 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Aberrant neurovascular coupling in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: Evidence from a multi-model MRI analysis.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 10;16:1050772. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1050772. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36703998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ziccardi L., Sadun F., De Negri A.M., Barboni P., Savini G., Borrelli E., Morgia C.L., Carelli V., Parisi V. Retinal function and neural conduction along the visual pathways in affected and unaffected carriers with Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013;54:6893. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12894. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

