Localization (and profiles) of tyrosinephosphorylated proteins in female reproductive organs of adult rats
- PMID: 32911588
- PMCID: PMC7482952
- DOI: 10.5653/cerm.2020.03573
Localization (and profiles) of tyrosinephosphorylated proteins in female reproductive organs of adult rats
Abstract
Objective: Tyrosine phosphorylation is an essential process in many biological systems, including the male reproductive system. The presence of tyrosine-phosphorylated (TyrPho) proteins has been well documented in male reproductive organs, but research in fertile females is still limited.
Methods: The ovary, oviduct, and uterus of adult female Sprague-Dawley rats in the estrus phase were used to localize TyrPho proteins using an immunohistochemical technique. These proteins were separated and their expression patterns were examined by sodium dodecyl sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blot analysis, respectively.
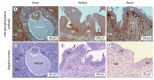
Results: TyrPho proteins were localized in the cytoplasm of the oocyte except the antral fluid; in the granulosa cells, theca cells, and stromal cells of the ovary; at the apical surface of oviductal epithelial cells; and in the basal epithelium and submucosa of the uterine wall. Moreover, we found that 72-, 43-, and 28-kDa TyrPho proteins were localized in the ovary, while 170-, 55-, and 43-kDa proteins were localized in the oviduct. In the uterus, we detected four major bands, corresponding to 61-, 55-, 54-, and 43-kDa TyrPho proteins.
Conclusion: Given that these TyrPho proteins were found in major reproductive organs in the estrus phase, these proteins may play important roles in female fertility.
Keywords: Ovary; Oviduct, Phosphorylation; Rats; Uterus.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic stress increases the tyrosine phosphorylation in female reproductive organs: An experimental study.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2021 Jan 25;19(1):87-96. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v19i1.8183. eCollection 2021 Jan. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2021. PMID: 33554006 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical localization of taurine in the rat ovary, oviduct, and uterus.J Histochem Cytochem. 2001 Sep;49(9):1133-42. doi: 10.1177/002215540104900907. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001. PMID: 11511682
-
Oviductal extracellular vesicles (oviductosomes, OVS) are conserved in humans: murine OVS play a pivotal role in sperm capacitation and fertility.Mol Hum Reprod. 2018 Mar 1;24(3):143-157. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gay003. Mol Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29370405 Free PMC article.
-
Amounts of an estrogen receptor β isoform increased in the theca of preovulatory follicles of sheep.Anim Reprod Sci. 2012 Apr;131(3-4):143-52. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Mar 10. Anim Reprod Sci. 2012. PMID: 22464186
-
Insulin-like peptide 3 (INSL3) is a major regulator of female reproductive physiology.Hum Reprod Update. 2018 Nov 1;24(6):639-651. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy029. Hum Reprod Update. 2018. PMID: 30204868 Review.
References
-
- Keller N, Ozmadenci D, Ichim G, Stupack D. Caspase-8 function, and phosphorylation, in cell migration. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;82:105–17. - PubMed
-
- Grindheim AK, Saraste J, Vedeler A. Protein phosphorylation and its role in the regulation of Annexin A2 function. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(11 Pt A):2515–29. - PubMed
-
- Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988;241:42–52. - PubMed
-
- Ullrich A, Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990;61:203–12. - PubMed
-
- Arad-Dann H, Beller U, Haimovitch R, Gavrieli Y, Ben-Sasson SA. Immunohistochemistry of phosphotyrosine residues: identification of distinct intracellular patterns in epithelial and steroidogenic tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993;41:513–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

