Exploration of inhibitory action of Azo imidazole derivatives against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro): A computational study
- PMID: 32904625
- PMCID: PMC7456803
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129178
Exploration of inhibitory action of Azo imidazole derivatives against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro): A computational study
Abstract
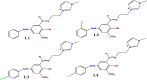
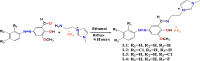
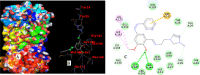
Four novel ionic liquid tagged azo-azomethine derivatives (L1-L4) have been prepared by the condensation reaction of azo-coupled ortho-vaniline precursor with amino functionalised imidazole derivative and the synthesized derivatives (L1-L4) have been characterized by different analytical and spectroscopic techniques. Molecular docking studies were carried out to ascertain the inhibitory action of studied ligands (L1-L4) against the Main Protease (6LU7) of novel coronavisrus (COVID-19). The result of the docking of L1-L4 showed a significant inhibitory action against the Main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 and the binding energy (ΔG) values of the ligands (L1-L4) against the protein 6LU7 have found to be -7.7 Kcal/mole (L1), -7.0 Kcal/mole (L2), -7.9 Kcal/mole (L3), and -7.9 Kcal/mole (L4).The efficiency of the ligands has been compared with the FDA approved and clinically trial drugs such as remdesivir, Chloroquin and Hydroxychloroquin and native ligand N3 of main protease 6LU7 to ascertain the inhibitory potential of the studied ligands (L1-L4) against the protein 6LU7. Pharmacokinetic properties (ADME) of the ligands (L1-L4) have also been studied.
Keywords: Azo imidazole; Binding energy; Chloroquin; Hydroxychloroquin; Molecular docking; Pharmacokinetics; Remdesivir; SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis, characterization and computational study on potential inhibitory action of novel azo imidazole derivatives against COVID-19 main protease (Mpro: 6LU7).J Mol Struct. 2021 Feb 5;1225:129230. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129230. Epub 2020 Sep 18. J Mol Struct. 2021. PMID: 32963413 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Effective Therapeutic Molecule from Natural Sources against Coronavirus Protease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;22(17):9431. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179431. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502340 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the inhibitory potential of novel piperidine-derivatives against main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2: A hybrid approach consisting of molecular docking, MD simulations and MMPBSA analysis.J Mol Liq. 2023 Jul 15;382:121904. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2023.121904. Epub 2023 Apr 26. J Mol Liq. 2023. PMID: 37151376 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory potential of repurposed drugs against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease: a computational-aided approach.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 May;40(8):3416-3427. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1847197. Epub 2020 Nov 17. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33200673 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Construction of Aroyl-Hydrazone Derivatives: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Molecular Docking and Their Biological Activities.Chem Biodivers. 2019 Nov;16(11):e1900315. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201900315. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Chem Biodivers. 2019. PMID: 31532059
Cited by
-
Comparative study of the interaction of ivermectin with proteins of interest associated with SARS-CoV-2: A computational and biophysical approach.Biophys Chem. 2021 Nov;278:106677. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106677. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Biophys Chem. 2021. PMID: 34428682 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, computational analyses, in silico ADMET studies, and inhibitory action against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) of a Schiff base.Turk J Chem. 2022 Jun 2;46(5):1548-1564. doi: 10.55730/1300-0527.3460. eCollection 2022. Turk J Chem. 2022. PMID: 37529731 Free PMC article.
-
Methodology-Centered Review of Molecular Modeling, Simulation, and Prediction of SARS-CoV-2.Chem Rev. 2022 Jul 13;122(13):11287-11368. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00965. Epub 2022 May 20. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35594413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural deformability induced in proteins of potential interest associated with COVID-19 by binding of homologues present in ivermectin: Comparative study based in elastic networks models.J Mol Liq. 2021 Oct 15;340:117284. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117284. Epub 2021 Aug 17. J Mol Liq. 2021. PMID: 34421159 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Specific Fluoroquinolone Interaction with SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) to Battle COVID-19: DFT, Molecular Docking, ADME and Cardiotoxicity Studies.Molecules. 2024 Oct 5;29(19):4721. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194721. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacIntyre C.R. Global spread of COVID-19 and pandemic potential. Global Biosecurity. 2020;1(3) doi: 10.31646/gbio.55. - DOI
-
- Li W.H., Moore M.J., Vasilieva N., Sui J.H., Wong S.K., Berne M.A., Somasundaran M., Sullivan J.L., Luzuriaga K., Greenough T.C., Choe H., Farzan M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426:450–454. doi: 10.1038/nature02145. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harismah K., Mirzaei M. Favipiravir: structural Analysis and Activity against COVID-19. Adv. J. Chem. Section B. 2020;2(2):55–60. doi: 10.33945/SAMI/AJCB.2020.2.3. - DOI
-
- Jin Z., Du X., Xu Y., Deng Y., Liu M., Zhao Y., Zhang B., Li X., Zhang L., Peng C., Duan Y., Yu J., Wang L., Yang K., Liu F., Jiang R., Yang X., You T., Liu X., Yang X., Bai F., Liu H., Liu X., Guddat L.W., Xu W., Xiao G., Qin C., Shi Z., Jiang H., Rao Z., Yang H. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature. 2020:1–24. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

