All-trans retinoic acid in non-promyelocytic acute myeloid leukemia: driver lesion dependent effects on leukemic stem cells
- PMID: 32900260
- PMCID: PMC7644151
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1810402
All-trans retinoic acid in non-promyelocytic acute myeloid leukemia: driver lesion dependent effects on leukemic stem cells
Abstract
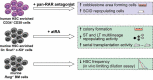
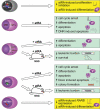
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive, often fatal hematopoietic malignancy. All-trans retinoic acid (atRA), one of the first molecularly targeted drugs in oncology, has greatly improved the outcome of a subtype of AML, acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). In contrast, atRA has so far provided little therapeutic benefit in the much larger group of patients with non-APL AML. Attempts to identify genetically or molecularly defined subgroups of patients that may respond to atRA have not yielded consistent results. Since AML is a stem cell-driven disease, understanding the effectiveness of atRA may require an appreciation of its impact on AML stem cells. Recent studies reported that atRA decreased stemness of AML with an FLT3-ITD mutation, yet increased it in AML1-ETO driven or EVI1-overexpressing AML. This review summarizes the role of atRA in normal hematopoiesis and in AML, focusing on its impact on AML stem cells.
Keywords: AML; FLT3; MECOM; atRA; hematopoietic stem cell; leukemia stem cell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evi1 Counteracts Anti-Leukemic and Stem Cell Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid on Flt3-ITD/Npm1c-Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.Biomedicines. 2020 Sep 28;8(10):385. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100385. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32998330 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide and all-trans-retinoic acid selectively exert synergistic cytotoxicity against FLT3-ITD AML cells via co-inhibition of FLT3 signaling pathways.Leuk Lymphoma. 2017 Oct;58(10):2426-2438. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1289522. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017. PMID: 28276286
-
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Activity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Role of Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Expression by the Microenvironment.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0127790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127790. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26047326 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming acute myeloid leukemia into sensitivity for retinoic-acid-driven differentiation.Exp Hematol. 2017 Aug;52:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28456748 Review.
-
Unlocking the potential of retinoic acid in anticancer therapy.Br J Cancer. 2014 Nov 25;111(11):2039-45. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.412. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25412233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Use of Valproic Acid and All-Trans Retinoic Acid in Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Literature Review and Discussion of Possible Use in Relapse after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 May 2;14(5):423. doi: 10.3390/ph14050423. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids: A Myth or a Reality for Cancer Therapy?Molecules. 2021 Jun 11;26(12):3583. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123583. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34208196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
All-trans retinoic acid induces differentiation in primary acute myeloid leukemia blasts carrying an inversion of chromosome 16.Int J Hematol. 2022 Jan;115(1):43-53. doi: 10.1007/s12185-021-03224-5. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Int J Hematol. 2022. PMID: 34546543
-
Current Understanding of Flavonoids in Cancer Therapy and Prevention.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 27;13(4):481. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040481. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Studies of Primary Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Derived from Patients Before and during Disease-Stabilizing Treatment Based on All-Trans Retinoic Acid and Valproic Acid.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;13(9):2143. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092143. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng S, Mitchell A, Kennedy J, et al. A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia. Nature. 2016;540:433–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
