Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 32891867
- PMCID: PMC8107826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115627
Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles
Abstract
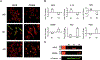
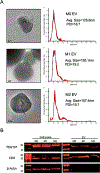
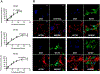
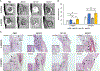
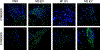
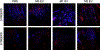
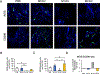
Multiple local and systemic factors including inflammation influence bone regeneration. Several lines of evidence demonstrate that macrophages contribute to the immunological regulation of MSC and osteoblast function during bone regeneration. Recent studies demonstrate that macrophage polarization influences this regulatory process. In this manuscript, we investigated the paracrine functional role of naïve (M0), M1 and M2 polarized macrophage derived EVs in bone repair. Treatment of rat calvaria defects with no EVs, M0 EVs, M1 EVs, or M2 EVs revealed polarization-specific control of bone regeneration by macrophage EVs at 3 and 6 weeks. M0 and M2 EVs promoted repair/regeneration and M1 EVs inhibited bone repair. Pathway-specific studies conducted in cell culture showed that M1 EVs negatively regulated the BMP signaling pathway, specifically BMP2 and BMP9. In parallel, miRNA sequencing studies showed similar miRNA cargo in M0 and M2 EVs and different miRNA cargo in M1 EVs. Functional examination of M1 macrophage EV-enriched miR-155 demonstrated that miR-155 mimic treatment reduced MSC osteogenic differentiation as measured by reduced BMP2, BMP9 and RUNX2 expression when compared to controls. Conversely, treatment of MSCs with the M2 macrophage EV-enriched miR-378a mimic increased MSC osteoinductive gene expression when compared to controls. These functional studies implicate polarized macrophage EV miRNAs in the positive or negative regulation of bone regeneration that was observed in vivo. Overall, the results presented in this study indicate that macrophage polarization influences EV cargo and related EV function in the paracrine regulation of bone regeneration.
Keywords: Bone repair; Exosomes; Extracellular vesicles; Macrophages; Monocytes.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
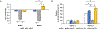
Similar articles
-
Functionally engineered extracellular vesicles improve bone regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jun;109:182-194. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.04.017. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32305445 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Primed Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Loaded on Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Biomaterial Exhibit Enhanced Macrophage Polarization.Cells. 2022 Jan 29;11(3):470. doi: 10.3390/cells11030470. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159282 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote cardiac repair after myocardial infarction via shifting macrophage polarization by targeting microRNA-139-3p/Stat1 pathway.BMC Med. 2023 Mar 16;21(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02778-x. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 36927608 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases.Cells. 2019 Dec 11;8(12):1605. doi: 10.3390/cells8121605. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31835680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Tissue Regeneration.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720908500. doi: 10.1177/0963689720908500. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32207341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
No small matter: emerging roles for exosomal miRNAs in the immune system.FEBS J. 2022 Jul;289(14):4021-4037. doi: 10.1111/febs.16052. Epub 2021 Jun 19. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34087046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genetic Aspects of Periodontitis Pathogenesis and the Regenerative Properties of Stem Cells.Cells. 2024 Jan 9;13(2):117. doi: 10.3390/cells13020117. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38247810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Hydrogels and Their Applications in Craniomaxillofacial Bone Regeneration.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 31;15(1):150. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010150. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune landscape and prognostic index for pancreatic cancer based on TCGA database and in vivo validation.BMC Cancer. 2023 Feb 10;23(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10597-9. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36765322 Free PMC article.
-
The Immuno-Modulation Effect of Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 16;12:785728. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.785728. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34975877 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

