Recombinant adiponectin protects the newborn rat lung from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury
- PMID: 32889775
- PMCID: PMC7507528
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14553
Recombinant adiponectin protects the newborn rat lung from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury
Abstract
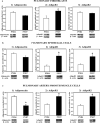
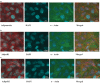
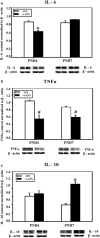
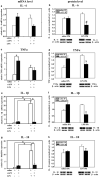
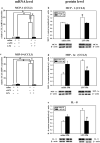
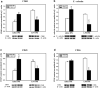
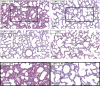
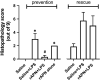
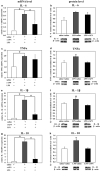
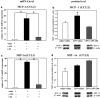
Preterm infants are at high risk for developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary hypertension from inflammatory lung injury. In adult models, adiponectin (APN)-an adipocyte-derived hormone-protects the lung from inflammatory injury and pulmonary vascular remodeling. Cord blood APN levels in premature infants born < 26 weeks gestation are 5% of the level in infants born at term. We previously reported the expression profile of APN and its receptors in neonatal rat lung homogenates during the first 3 weeks of postnatal development. Here, we characterize the expression profile of APN and its receptors in specific lung cells and the effects of exogenous recombinant APN (rAPN) on lipopolysaccharide-(LPS)-induced cytokine and chemokine production in total lung homogenates and specific lung cells. In vitro, rAPN added to primary cultures of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells attenuated the expression of LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines while increasing the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines. In vivo, intraperitoneal rAPN (2 mg/kg), given 4 hr prior to intrapharyngeal administration of LPS (5 mg/kg) to newborn rats at postnatal day 4, significantly reduced gene and protein expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1ß and reduced protein expression of the chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α) in the lung. LPS-induced histopathological changes in the lung were also decreased. Moreover, rAPN given 20 hr after intrapharyngeal LPS had a similar effect on lung inflammation. These findings suggest a role for APN in protecting the lung from inflammation during early stages of lung development.
Keywords: adiponectin; adiponectin receptors 1 and 2; bronchopulmonary dysplasia; chemokines; cytokines; neonatal rat.
© 2020 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Premature Infants: The Link Between Low Fat Stores, Adiponectin Receptor Signaling and Lung Injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1071:151-157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91137-3_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30357746
-
Effects of adiponectin on acute lung injury in cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis rats.J Surg Res. 2013 Aug;183(2):752-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.01.055. Epub 2013 Feb 16. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23522481
-
Effect of Intranasal Instillation of Lipopolysaccharide on Lung Development and Its Related Mechanism in Newborn Mice.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019 Nov;39(11):684-693. doi: 10.1089/jir.2019.0006. Epub 2019 Jul 3. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019. PMID: 31268385 Free PMC article.
-
The role of adiponectin in periodontitis: Current state and future prospects.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111358. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111358. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33561644 Review.
-
The potential molecular implications of adiponectin in the evolution of SARS-CoV-2: Inbuilt tendency.J King Saud Univ Sci. 2022 Nov;34(8):102347. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102347. Epub 2022 Sep 30. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2022. PMID: 36211634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unleashing AdipoRon's Potential: A Fresh Approach to Tackle Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections in Bronchiectasis via Sphingosine Metabolism Modulation.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 24;17:7653-7674. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S483689. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39469062 Free PMC article.
-
PGC-1α activity and mitochondrial dysfunction in preterm infants.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 26;13:997619. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.997619. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36225305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maturational effect of leptin on CO2 chemosensitivity in newborn rats.Pediatr Res. 2023 Sep;94(3):971-978. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02604-3. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 37185965
References
-
- Ambalavanan, N. , Carlo, W. A. , D'Angio, C. T. , McDonald, S. A. , Das, A. , Schendel, D. , … Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child H, Human Development Neonatal Research N . (2009). Cytokines associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics, 123(4), 1132–1141. 10.1542/peds.2008-0526 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

