Systems-level differential gene expression analysis reveals new genetic variants of oral cancer
- PMID: 32887903
- PMCID: PMC7473858
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71346-7
Systems-level differential gene expression analysis reveals new genetic variants of oral cancer
Abstract
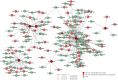
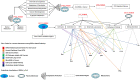
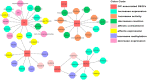
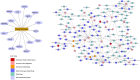
Oral cancer (OC) ranked as eleventh malignancy worldwide, with the increasing incidence among young patients. Limited understanding of complications in cancer progression, its development system, and their interactions are major restrictions towards the progress of optimal and effective treatment strategies. The system-level approach has been designed to explore genetic complexity of the disease and to identify novel oral cancer related genes to detect genomic alterations at molecular level, through cDNA differential analysis. We analyzed 21 oral cancer-related cDNA datasets and listed 30 differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Among 30, we found 6 significant DEGs including CYP1A1, CYP1B1, ADCY2, C7, SERPINB5, and ANAPC13 and studied their functional role in OC. Our genomic and interactive analysis showed significant enrichment of xenobiotics metabolism, p53 signaling pathway and microRNA pathways, towards OC progression and development. We used human proteomic data for post-translational modifications to interpret disease mutations and inter-individual genetic variations. The mutational analysis revealed the sequence predicted disordered region of 14%, 12.5%, 10.5% for ADCY2, CYP1B1, and C7 respectively. The MiRNA target prediction showed functional molecular annotation including specific miRNA-targets hsa-miR-4282, hsa-miR-2052, hsa-miR-216a-3p, for CYP1B1, C7, and ADCY2 respectively associated with oral cancer. We constructed the system level network and found important gene signatures. The drug-gene interaction of OC source genes with seven FDA approved OC drugs help to design or identify new drug target or establishing novel biomedical linkages regarding disease pathophysiology. This investigation demonstrates the importance of system genetics for identifying 6 OC genes (CYP1A1, CYP1B1, ADCY2, C7, SERPINB5, and ANAPC13) as potential drugs targets. Our integrative network-based system-level approach would help to find the genetic variants of OC that can accelerate drug discovery outcomes to develop a better understanding regarding treatment strategies for many cancer types.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
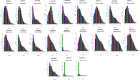

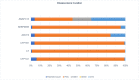
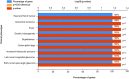
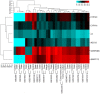


Similar articles
-
Integrated Analysis and MicroRNA Expression Profiling Identified Seven miRNAs Associated With Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Aug;232(8):2178-2185. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25728. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27935034
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for the screening of hub genes and therapeutic drugs in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2020 Jan 27;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-0613-2. J Ovarian Res. 2020. PMID: 31987036 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis of mRNAs and miRNAs Identified Potential Biomarkers of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Jun 29;21(6):1841-1848. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.6.1841. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32597160 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the role of miRNAs in oral cancer pathogenesis: A focus on signaling pathways.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Dec;252:154949. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154949. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37992507 Review.
-
Cancer systems biology: exploring cancer-associated genes on cellular networks.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Jul;64(14):1752-62. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7054-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17415519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide Meta-analysis Reveals New Gene Signatures and Potential Drug Targets of Hypertension.ACS Omega. 2022 Jun 20;7(26):22754-22772. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02277. eCollection 2022 Jul 5. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35811894 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis Demonstrates the Prognostic Value of Chromatin Accessibility Biomarkers in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 21;11:814396. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.814396. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34993155 Free PMC article.
-
Multicellular biomarkers of drug resistance as promising targets for glioma precision medicine and predictors of patient survival.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 2;5(2):511-533. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2021.145. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35800363 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CDH2 and MCP-1 mRNAs of blood extracellular vesicles in predicting early-stage diabetic nephropathy.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 1;17(4):e0265619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265619. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35363774 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the role of heavy metals xenobiotics in cancer: a critical review.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 4;15(1):615. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01417-y. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39495398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khawaja MR, et al. Chewing of betel, areca and tobacco: Perceptions and knowledge regarding their role in head and neck cancers in an urban squatter settlement in Pakistan. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2006;7:95–100. - PubMed
-
- Bhurgri Y, Bhurgri A, Usman A. Epidemiological review of head and neck cancers in Karachi. Asian Pac. J. 2006;7:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Masood N, Kayani MA, Malik FA, Baig RM, Faryal R. Genetic variations in carcinogen metabolizing genes associated with oral cancer in pakistani population. Asia. Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011;12:491–495. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

