RPL-4 and RPL-9 ̶Mediated Ribosome Purifications Facilitate the Efficient Analysis of Gene Expression in Caenorhabditis elegans Germ Cells
- PMID: 32883755
- PMCID: PMC7642943
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.120.401644
RPL-4 and RPL-9 ̶Mediated Ribosome Purifications Facilitate the Efficient Analysis of Gene Expression in Caenorhabditis elegans Germ Cells
Abstract
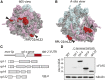
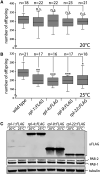
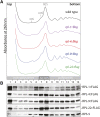
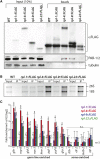
In many organisms, tissue complexity and cellular diversity create a barrier that can hinder our understanding of gene expression programs. To address this problem, methods have been developed that allow for easy isolation of translated mRNAs from genetically defined cell populations. A prominent example is the Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification method also called TRAP. Here, ribosome associated mRNAs are isolated via purification of the ribosomal protein RPL10A/uL1, which is expressed under the control of a tissue specific promoter. Originally developed to investigate gene expression in mouse neurons, it has by now been adopted to many different organisms and tissues. Interestingly, TRAP has never been used successfully to analyze mRNA translation in germ cells. Employing a combination of genetic and biochemical approaches, I assessed several ribosomal proteins for their suitability for TRAP using the Caenorhabditis elegans germline as a target tissue. Surprisingly, I found that RPL10A/uL1 is not the ideal ribosomal component to perform such an analysis in germ cells. Instead other proteins such as RPL4/uL4 or RPL9/eL6 are much better suited for this task. Tagged variants of these proteins are well expressed in germ cells, integrated into translating ribosomes and do not influence germ cell functions. Furthermore, germ cell-specific mRNAs are much more efficiently co-purified with RPL4/uL4 and RPL9/uL6 compared to RPL10A/uL1. This study provides a solid basis upon which future germ cell TRAP experiments can be built, and it highlights the need for rigorous testing when adopting such methods to a new biological system.
Keywords: gene expression; germ cell; ribosomal protein; translation.
Copyright © 2020 Nousch.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A single-copy knockin translating ribosome immunoprecipitation toolkit for tissue-specific profiling of actively translated mRNAs in C. elegans.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Mar 27;3(3):100433. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100433. eCollection 2023 Mar 27. Cell Rep Methods. 2023. PMID: 37056370 Free PMC article.
-
Cell type-specific transcriptome profiling in C. elegans using the Translating Ribosome Affinity Purification technique.Methods. 2017 Aug 15;126:130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.06.023. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28648677
-
LIN-35/Rb causes starvation-induced germ cell apoptosis via CED-9/Bcl2 downregulation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;34(13):2499-516. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01532-13. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24752899 Free PMC article.
-
Translational control in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:205-47. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872479 Review.
-
Dynamic regulation of ribosome levels and translation during development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 28;136:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.06.004. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35725716 Review.
Cited by
-
The 18S rRNA Methyltransferase DIMT-1 Regulates Lifespan in the Germline Later in Life.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 15:2024.05.14.594211. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.14.594211. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38798397 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The 18S rRNA Methyltransferase DIMT-1 Regulates Lifespan in the Germline Later in Life.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 21:rs.3.rs-4421268. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4421268/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38946979 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A single-copy knockin translating ribosome immunoprecipitation toolkit for tissue-specific profiling of actively translated mRNAs in C. elegans.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Mar 27;3(3):100433. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100433. eCollection 2023 Mar 27. Cell Rep Methods. 2023. PMID: 37056370 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
