Membrane Association and Functional Mechanism of Synaptotagmin-1 in Triggering Vesicle Fusion
- PMID: 32882186
- PMCID: PMC7499113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.08.008
Membrane Association and Functional Mechanism of Synaptotagmin-1 in Triggering Vesicle Fusion
Abstract
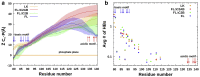
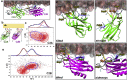
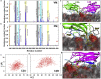
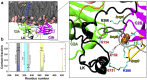
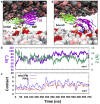
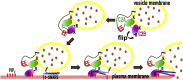
Upon Ca2+ influx, synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic plasma membrane (PM) to release neurotransmitters. Membrane fusion is triggered by synaptotagmin-1, a transmembrane protein in the vesicle membrane (VM), but the mechanism is under debate. Synaptotagmin-1 contains a single transmembrane helix (TM) and two tandem C2 domains (C2A and C2B). This study aimed to use molecular dynamics simulations to elucidate how Ca2+-bound synaptotagmin-1, by simultaneously associating with VM and PM, brings them together for fusion. Although C2A stably associates with VM via two Ca2+-binding loops, C2B has a propensity to partially dissociate. Importantly, an acidic motif in the TM-C2A linker competes with VM for interacting with C2B, thereby flipping its orientation to face PM. Subsequently, C2B readily associates with PM via a polybasic cluster and a Ca2+-binding loop. The resulting mechanistic model for the triggering of membrane fusion by synaptotagmin-1 reconciles many experimental observations.
Copyright © 2020 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polybasic Patches in Both C2 Domains of Synaptotagmin-1 Are Required for Evoked Neurotransmitter Release.J Neurosci. 2022 Jul 27;42(30):5816-5829. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1385-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35701163 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of synaptotagmin C2 domain specificity in regulating spontaneous and evoked neurotransmitter release.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 2;33(1):187-200. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3214-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23283333 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-1 C2B domain interacts simultaneously with SNAREs and membranes to promote membrane fusion.Elife. 2016 Apr 15;5:e14211. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14211. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27083046 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+-Triggered Synaptic Vesicle Fusion Initiated by Release of Inhibition.Trends Cell Biol. 2018 Aug;28(8):631-645. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Trends Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29706534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The C2 domains of synaptotagmin--partners in exocytosis.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Mar;29(3):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.01.008. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15003272 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic formation of the protein-lipid prefusion complex.Biophys J. 2024 Oct 15;123(20):3569-3586. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.09.009. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 39257001
-
The structure and flexibility analysis of the Arabidopsis synaptotagmin 1 reveal the basis of its regulation at membrane contact sites.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Aug 18;4(10):e202101152. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101152. Print 2021 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34408000 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Formation of the Protein-Lipid Pre-fusion Complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 11:2024.04.17.589983. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.17.589983. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biophys J. 2024 Oct 15;123(20):3569-3586. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.09.009 PMID: 38659925 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Fuzzy Association of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein with Acidic Membranes.JACS Au. 2021 Jan 25;1(1):66-78. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.0c00039. Epub 2020 Dec 9. JACS Au. 2021. PMID: 33554215 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Proteins Regulating Synaptic Vesicle Fusion.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;13(3):307. doi: 10.3390/membranes13030307. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984694 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

