Nontoxic-dose deoxynivalenol aggravates lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammation and tight junction disorder in IPEC-J2 cells through activation of NF-κB and LC3B
- PMID: 32877744
- PMCID: PMC7456579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111712
Nontoxic-dose deoxynivalenol aggravates lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammation and tight junction disorder in IPEC-J2 cells through activation of NF-κB and LC3B
Abstract
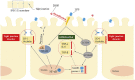
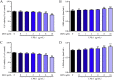
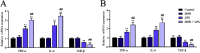
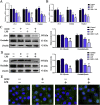
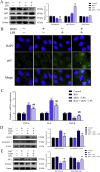
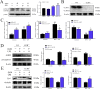
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is the key factor in various intestinal inflammation which could disrupt the epithelial barrier function. Deoxynivalenol (DON), a well-known mycotoxin, can induce intestinal injury. However, the combined enterotoxicity of LPS and DON has rarely been studied. In this study, IPEC-J2 cell monolayers were exposed to LPS and nontoxic-dose DON for 12 and 24 h to investigate the effects of DON on LPS-induced inflammatory response and tight junction variation, and specific inhibitor and CRISPR-Cas9 were used to explore the underlying mechanisms. Our results showed that nontoxic-dose DON aggravated LPS-induced cellular inflammatory response, reflecting on more significant changes of inflammatory cytokines mRNA expression, higher protein expression of NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) and procaspase-1. Moreover, nontoxic-dose DON aggravated LPS-induced mRNA and protein expression decreased, and distribution confused of tight junction proteins. We found that DON further enhanced LPS-induced phosphorylation and nucleus translocation of p65, and expression of LC3B-Ⅱ. NF-κB inhibitor and CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of LC3B attenuated the effects of combination which indicated nontoxic-dose DON aggravated LPS-induced intestinal inflammation and tight junction disorder through activating NF-κB signaling pathway and autophagy-related protein LC3B. It further warns that ingesting low doses of mycotoxins may exacerbate the effects of intestinal pathogens on the body.
Keywords: Deoxynivalenol; Inflammation; LC3B; LPS; NF-κB signaling pathway; Tight junction.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nontoxic concentrations of OTA aggravate DON-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in IPEC-J2 cells via activation of NF-κB signaling pathway.Toxicol Lett. 2019 Sep 1;311:114-124. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.04.021. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Toxicol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31026484
-
Nontoxic dose of Phenethyl isothiocyanate ameliorates deoxynivalenol-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation in IPEC-J2 cells.Res Vet Sci. 2021 May;136:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.02.002. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Res Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33588096
-
Effects of Deoxynivalenol and Mycotoxin Adsorbent Agents on Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways and Inflammation-Associated Gene Expression in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;13(5):301. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050301. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922863 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic mechanisms of the trichothecenes T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol on protein synthesis.Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 Jun;164:113044. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113044. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35452771 Review.
-
Deoxynivalenol: Emerging Toxic Mechanisms and Control Strategies, Current and Future Perspectives.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jul 26;71(29):10901-10915. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02020. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37437258 Review.
Cited by
-
Constitutively active microglial populations limit anorexia induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Nov 19;19(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02631-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36403004 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal Enterotoxin A Induces Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction and Activates NLRP3 Inflammasome via NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathways in Mice.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jan 1;14(1):29. doi: 10.3390/toxins14010029. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35051006 Free PMC article.
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate as an anti-nutritional factor attenuates deoxynivalenol-induced IPEC-J2 cell injury through inhibiting ROS-mediated autophagy.Anim Nutr. 2022 Mar;8(1):300-309. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.09.013. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Anim Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35024467 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Mycotoxin-Induced Toxicological Mechanisms.Vet Sci. 2024 Jun 28;11(7):291. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11070291. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39057975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ochratoxin A induces nephrotoxicity in vitro and in vivo via pyroptosis.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Apr;95(4):1489-1502. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-02993-6. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33543323
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

