Rab35 Targeting to the Plasma Membrane Is Dependent on the C-terminal Polybasic Cluster
- PMID: 32873993
- PMCID: PMC7450177
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.20-00006
Rab35 Targeting to the Plasma Membrane Is Dependent on the C-terminal Polybasic Cluster
Abstract
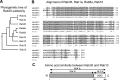
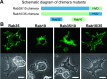
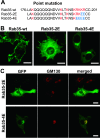
Rab35, a member of the Rab GTPase family, has been implicated in various cellular processes including cell motility and membrane trafficking. Although Rab35 is localized to the plasma membrane, Rab proteins that are identified to have high sequence homology with Rab35 exhibit distinct subcellular localization patterns. Comparing the amino acid sequences between Rab35 and its family members revealed a significant variation in an approximate 30-amino acid region of the C-terminus. This suggests that this region determines the subcellular localization of individual Rab proteins. To confirm this hypothesis, we constructed Rab35-Rab10 chimera proteins by exchanging their C-terminal domains with one another. Confocal microscopy of RAW264 cells expressing EGFP-fused Rab35-Rab10 chimeras has indicated that the C-terminal region of Rab35 is critical for its plasma membrane localization. Furthermore, we were able to determine that a basic amino acid cluster exists in the C-terminal region of Rab35 and that Rab35 localization shifts to the Golgi membrane when the number of basic amino acids in this region is reduced. Thus, it is likely that the approximate 30-amino acid C-terminal region containing basic clusters is responsible for Rab35 plasma membrane localization and that its preferential localization depends on the number of basic amino acids.
Keywords: C-terminus; Rab35; basic clusters; confocal microscopy; plasma membrane.
2020 The Japan Society of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
IVThe authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rab35 GTPase: A Central Regulator of Phosphoinositides and F-actin in Endocytic Recycling and Beyond.Traffic. 2016 Oct;17(10):1063-77. doi: 10.1111/tra.12422. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Traffic. 2016. PMID: 27329675 Review.
-
Characterization of the nuclear localization signal in the DNA helicase responsible for Bloom syndrome.Int J Mol Med. 2000 May;5(5):477-84. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.5.5.477. Int J Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 10762650
-
Rab35/ACAP2 and Rab35/RUSC2 Complex Structures Reveal Molecular Basis for Effector Recognition by Rab35 GTPase.Structure. 2019 May 7;27(5):729-740.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Structure. 2019. PMID: 30905672
-
An ARF6/Rab35 GTPase cascade for endocytic recycling and successful cytokinesis.Curr Biol. 2012 Jan 24;22(2):147-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.11.058. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22226746
-
Rab35 GTPase and cancer: Linking membrane trafficking to tumorigenesis.Traffic. 2018 Apr;19(4):247-252. doi: 10.1111/tra.12546. Epub 2018 Feb 11. Traffic. 2018. PMID: 29314576 Review.
Cited by
-
Rab35 GTPase positively regulates endocytic recycling of cardiac KATP channels.Channels (Austin). 2022 Dec;16(1):137-147. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2022.2090667. Channels (Austin). 2022. PMID: 35754325 Free PMC article.
-
Rab10-Positive Tubular Structures Represent a Novel Endocytic Pathway That Diverges From Canonical Macropinocytosis in RAW264 Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2021 May 31;12:649600. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.649600. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34135890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bigay J. and Antonny B. (2012) Curvature, lipid packing, and electrostatics of membrane organelles: defining cellular territories in determining specificity. Dev. Cell 23; 886–895. - PubMed
-
- Chaineau M., Ioannou M. S. and McPherson P. S. (2013) Rab35: GEFs, GAPs and effectors. Traffic 14; 1109–1117. - PubMed
-
- Chavrier P., Gorvel J.-P., Stelzer E., Simons K., Gruenberg J. and Zerial M. (1991) Hypervariable C-terminal domain of rab proteins acts as a targeting signal. Nature 353; 769–772. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

