B cells expressing authentic naive human VRC01-class BCRs can be recruited to germinal centers and affinity mature in multiple independent mouse models
- PMID: 32873644
- PMCID: PMC7502816
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2004489117
B cells expressing authentic naive human VRC01-class BCRs can be recruited to germinal centers and affinity mature in multiple independent mouse models
Abstract
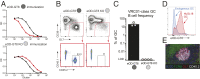
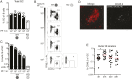
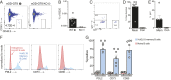
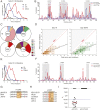
Animal models of human antigen-specific B cell receptors (BCRs) generally depend on "inferred germline" sequences, and thus their relationship to authentic naive human B cell BCR sequences and affinities is unclear. Here, BCR sequences from authentic naive human VRC01-class B cells from healthy human donors were selected for the generation of three BCR knockin mice. The BCRs span the physiological range of affinities found in humans, and use three different light chains (VK3-20, VK1-5, and VK1-33) found among subclasses of naive human VRC01-class B cells and HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). The germline-targeting HIV immunogen eOD-GT8 60mer is currently in clinical trial as a candidate bnAb vaccine priming immunogen. To attempt to model human immune responses to the eOD-GT8 60mer, we tested each authentic naive human VRC01-class BCR mouse model under rare human physiological B cell precursor frequency conditions. B cells with high (HuGL18HL) or medium (HuGL17HL) affinity BCRs were primed, recruited to germinal centers, and they affinity matured, and formed memory B cells. Precursor frequency and affinity interdependently influenced responses. Taken together, these experiments utilizing authentic naive human VRC01-class BCRs validate a central tenet of germline-targeting vaccine design and extend the overall concept of the reverse vaccinology approach to vaccine development.
Keywords: HIV; germinal center; germline targeting; immunodominance; vaccine.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: W.R.S. is an inventor on a patent application submitted by IAVI and The Scripps Research Institute that covers the eOD-GT8 immunogen. W.R.S. is involved as a principal investigator of a human clinical trial involving eOD-GT8 60mer (G001). As part of that involvement, W.R.S. is privy to certain clinical trial data, and he was forbidden from sharing that data with the authors of this study during the course of this HuGL study, as is standard for blinded clinical trials. Any conclusions in this manuscript regarding relationships between HuGL mouse models and humans were made by the other authors, without input from W.R.S. related to any clinical trial activities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The human naive B cell repertoire contains distinct subclasses for a germline-targeting HIV-1 vaccine immunogen.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Jul 4;10(448):eaat0381. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat0381. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29973404 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody precursor B cells revealed by germline-targeting immunogen.Science. 2016 Mar 25;351(6280):1458-63. doi: 10.1126/science.aad9195. Science. 2016. PMID: 27013733 Free PMC article.
-
Glycan Masking Focuses Immune Responses to the HIV-1 CD4-Binding Site and Enhances Elicitation of VRC01-Class Precursor Antibodies.Immunity. 2018 Aug 21;49(2):301-311.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 30076101 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies: VRC01 and Beyond.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1075:53-72. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0484-2_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030789 Review.
-
Discovery medicine - the HVTN's iterative approach to developing an HIV-1 broadly neutralizing vaccine.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023 Nov 1;18(6):290-299. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000821. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023. PMID: 37712873 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engaging an HIV vaccine target through the acquisition of low B cell affinity.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 28;14(1):5249. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40918-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37640732 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination in a humanized mouse model elicits highly protective PfCSP-targeting anti-malarial antibodies.Immunity. 2021 Dec 14;54(12):2859-2876.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.10.017. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 34788599 Free PMC article.
-
Rationalizing Random Walks: Replicating Protective Antibody Trajectories.Trends Immunol. 2021 Mar;42(3):186-197. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.01.001. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33514459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Affinity gaps among B cells in germinal centers drive the selection of MPER precursors.Nat Immunol. 2024 Jun;25(6):1083-1096. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01844-7. Epub 2024 May 30. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38816616 Free PMC article.
-
Germline-targeting HIV-1 Env vaccination induces VRC01-class antibodies with rare insertions.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Apr 18;4(4):101003. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101003. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37044090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloom D. E., Fan V. Y., Sevilla J. P., The broad socioeconomic benefits of vaccination. Sci. Transl. Med. 10, eaaj2345 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Plotkin S. A., Orenstein W. A., Offit P. A., Plotkin’s Vaccines (Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, ed. 7, 2018), p. 1691, pp. xxi.
-
- Havenar-Daughton C., Lee J. H., Crotty S., Tfh cells and HIV bnAbs, an immunodominance model of the HIV neutralizing antibody generation problem. Immunol. Rev. 275, 49–61 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Kwong P. D., Mascola J. R., HIV-1 vaccines based on antibody identification, B cell ontogeny, and epitope structure. Immunity 48, 855–871 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

