Paxillin family of focal adhesion adaptor proteins and regulation of cancer cell invasion
- PMID: 32859368
- PMCID: PMC7737098
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.05.003
Paxillin family of focal adhesion adaptor proteins and regulation of cancer cell invasion
Abstract
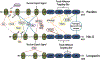
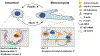
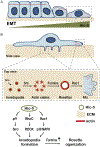
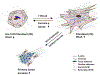
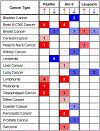
The paxillin family of proteins, including paxillin, Hic-5, and leupaxin, are focal adhesion adaptor/scaffolding proteins which localize to cell-matrix adhesions and are important in cell adhesion and migration of both normal and cancer cells. Historically, the role of these proteins in regulating the actin cytoskeleton through focal adhesion-mediated signaling has been well documented. However, studies in recent years have revealed additional functions in modulating the microtubule and intermediate filament cytoskeletons to affect diverse processes including cell polarization, vesicle trafficking and mechanosignaling. Expression of paxillin family proteins in stromal cells is also important in regulating tumor cell migration and invasion through non-cell autonomous effects on the extracellular matrix. Both paxillin and Hic-5 can also influence gene expression through a variety of mechanisms, while their own expression is frequently dysregulated in various cancers. Accordingly, these proteins may serve as valuable targets for novel diagnostic and treatment approaches in cancer.
Keywords: Actin; Hic-5; Invasion; Mechanosignaling; Migration; Paxillin; Plasticity; Stroma.
© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
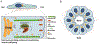
Similar articles
-
Distinct roles for paxillin and Hic-5 in regulating breast cancer cell morphology, invasion, and metastasis.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Feb 1;22(3):327-41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-09-0790. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21148292 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin and Hic-5 interaction with vinculin is differentially regulated by Rac1 and RhoA.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037990. Epub 2012 May 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22629471 Free PMC article.
-
Hic-5 expression is a major indicator of cancer cell morphology, migration, and plasticity in three-dimensional matrices.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Jul 15;29(13):1704-1717. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0092. Epub 2018 May 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29771639 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin: a crossroad in pathological cell migration.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Feb 18;10(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0418-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28214467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The explorations of dynamic interactions of paxillin at the focal adhesions.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2022 Oct 1;1870(10):140825. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2022.140825. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2022. PMID: 35926716 Review.
Cited by
-
Hic-5 regulates extracellular matrix-associated gene expression and cytokine secretion in cancer associated fibroblasts.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Feb 15;435(2):113930. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.113930. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38237846 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of holocarboxylase synthetase deficient-MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells revealed the biochemical changes associated with cell death, impaired growth signaling, and metabolism.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 11;10:1250423. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1250423. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38283944 Free PMC article.
-
An ULK1/2-PXN mechanotransduction pathway suppresses breast cancer cell migration.EMBO Rep. 2023 Nov 6;24(11):e56850. doi: 10.15252/embr.202356850. Epub 2023 Oct 17. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37846507 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Oncogenic Targets by the Tumor-Suppressive miR-139 Duplex (miR-139-5p and miR-139-3p) in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2020 Dec 12;8(12):599. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8120599. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33322675 Free PMC article.
-
Progerin Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Melanoma Cells by Regulating the Expression of Paxillin.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Mar 22;17:227-242. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S442504. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38533131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambadipudi S, Zweckstetter M, 2016. Targeting intrinsically disordered proteins in rational drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov 11, 65–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

