Positive allosteric modulation of the cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) in periaqueductal gray (PAG) antagonizes anti-nociceptive and cellular effects of a mu-opioid receptor agonist in morphine-withdrawn rats
- PMID: 32857187
- PMCID: PMC7687722
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-020-05650-5
Positive allosteric modulation of the cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) in periaqueductal gray (PAG) antagonizes anti-nociceptive and cellular effects of a mu-opioid receptor agonist in morphine-withdrawn rats
Abstract
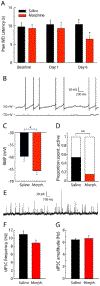
Opioid drugs are a first-line treatment for severe acute pain and other chronic pain conditions, but long-term opioid drug use produces opioid-induced hyperalgesia (OIH). Co-administration of cannabinoids with opioid receptor agonists produce anti-nociceptive synergy, but cannabinoid receptor agonists may also produce undesirable side effects. Therefore, positive allosteric modulators (PAM) of cannabinoid type-1 receptors (CB1R) may provide an option reducing pain and/or enhancing the anti-hyperalgesic effects of opioids without the side effects, tolerance, and dependence observed with the use of ligands that target the orthosteric binding sites. This study tested GAT211, a PAM of cannabinoid type-1 receptors (CB1R), for its ability to enhance the anti-hyperalgesic effects of the mu-opioid receptor (MOR) agonist DAMGO in rats treated chronically with morphine (or saline) and tested during withdrawal. We tested the effects of intra-periaqueductal gray (PAG) injections of (1) DAMGO, (2) GAT211, or (3) DAMGO + GAT211 on thermal nociception in chronic morphine-treated rats that were hyperalgesic and also in saline-treated control rats. We used slice electrophysiology to test the effects of DAMGO/GAT211 bath application on synaptic transmission in the vlPAG. Intra-PAG DAMGO infusions dose-dependently reversed chronic morphine-induced hyperalgesia, but intra-PAG GAT211 did not alter nociception at the doses we tested. When co-administered into the PAG, GAT211 antagonized the anti-nociceptive effects of DAMGO in morphine-withdrawn rats. DAMGO suppressed synaptic inhibition in the vlPAG of brain slices taken from saline- and morphine-treated rats, and GAT211 attenuated DAMGO-induced suppression of synaptic inhibition in vlPAG neurons via actions at CB1R. These findings show that positive allosteric modulation of CB1R antagonizes the behavioral and cellular effects of a MOR agonist in the PAG of rats.
Keywords: Dose-response; Hyperalgesia; Morphine; Opiates; Opioids; PAG; Pain; Positive allosteric modulators.
Figures

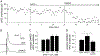
Similar articles
-
Repeated morphine treatment alters cannabinoid modulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission within the rat periaqueductal grey.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):681-90. doi: 10.1111/bph.12809. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24916363 Free PMC article.
-
Mu-opioid and CB1 cannabinoid receptors of the dorsal periaqueductal gray interplay in the regulation of fear response, but not antinociception.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Jul;194:172938. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172938. Epub 2020 May 3. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32376258
-
Low dose combination of morphine and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol circumvents antinociceptive tolerance and apparent desensitization of receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 1;571(2-3):129-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.06.001. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17603035 Free PMC article.
-
β-arrestins: regulatory role and therapeutic potential in opioid and cannabinoid receptor-mediated analgesia.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;219:427-43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41199-1_22. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24292843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands as Treatment for Substance Use Disorders.CNS Drugs. 2019 Oct;33(10):1001-1030. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00664-w. CNS Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31549358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Interventions for Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia: A Scoping Review of Preclinical Trials.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 29;11(23):7060. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237060. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498635 Free PMC article.
-
Short Tandem Repeat Variation in the CNR1 Gene Associated With Analgesic Requirements of Opioids in Postoperative Pain Management.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 3;13:815089. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.815089. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35360861 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid receptor 1 positive allosteric modulator ZCZ011 shows differential effects on behavior and the endocannabinoid system in HIV-1 Tat transgenic female and male mice.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 24;19(6):e0305868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305868. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38913661 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic potential of the type 1 cannabinoid receptor positive allosteric modulator GAT211: preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Apr;238(4):1087-1098. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05755-x. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33442771
-
HCN-Channel-Dependent Hyperexcitability of the Layer V Pyramidal Neurons in IL-mPFC Contributes to Fentanyl-Induced Hyperalgesia in Male Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 May;60(5):2553-2571. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03218-w. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36689134
References
-
- Alaverdashvili M and Laprairie RB (2018). “The future of type 1 cannabinoid receptor allosteric ligands.” Drug Metab Rev 50(1): 14–25. - PubMed
-
- Angst MS and Clark JD (2006). “Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: a qualitative systematic review.” Anesthesiology 104(3): 570–587. - PubMed
-
- Bagley EE, Gerke MB, Vaughan CW, Hack SP and Christie MJ (2005). “GABA transporter currents activated by protein kinase A excite midbrain neurons during opioid withdrawal.” Neuron 45(3): 433–445. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

