Regulation of mTORC1 by Upstream Stimuli
- PMID: 32854217
- PMCID: PMC7565831
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11090989
Regulation of mTORC1 by Upstream Stimuli
Abstract
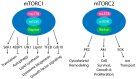
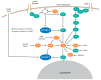
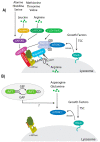
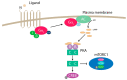
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is an evolutionary conserved Ser/Thr protein kinase that senses multiple upstream stimuli to control cell growth, metabolism, and autophagy. mTOR is the catalytic subunit of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1). A significant amount of research has uncovered the signaling pathways regulated by mTORC1, and the involvement of these signaling cascades in human diseases like cancer, diabetes, and ageing. Here, we review advances in mTORC1 regulation by upstream stimuli. We specifically focus on how growth factors, amino acids, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), phosphorylation, and small GTPases regulate mTORC1 activity and signaling.
Keywords: G-protein coupled receptors; amino acids; and autophagy; cell growth; kinases; mTORC1; metabolism; phosphorylation; small GTPases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
G-Protein Coupled Receptor Signaling and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Regulation.Mol Pharmacol. 2022 Apr;101(4):181-190. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000302. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34965982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino acid-dependent control of mTORC1 signaling: a variety of regulatory modes.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Aug 17;27(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00679-2. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32799865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RagC phosphorylation autoregulates mTOR complex 1.EMBO J. 2019 Feb 1;38(3):e99548. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899548. Epub 2018 Dec 14. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 30552228 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP13 couples GPCR signaling to mTORC1 inhibition.PLoS Genet. 2021 Oct 21;17(10):e1009832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009832. eCollection 2021 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34673774 Free PMC article.
-
GPCR signaling inhibits mTORC1 via PKA phosphorylation of Raptor.Elife. 2019 May 21;8:e43038. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43038. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31112131 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Alterations in Tau Protein Level and Phosphorylation State in the Brain of the Autistic-Like Rats Induced by Prenatal Exposure to Valproic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 22;22(6):3209. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063209. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809910 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutics That Can Potentially Replicate or Augment the Anti-Aging Effects of Physical Exercise.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 1;23(17):9957. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179957. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR signalling pathway in stem cell bioactivities and angiogenesis potential.Cell Prolif. 2023 Dec;56(12):e13499. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13499. Epub 2023 May 8. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 37156724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamine synthetase limits β-catenin-mutated liver cancer growth by maintaining nitrogen homeostasis and suppressing mTORC1.J Clin Invest. 2022 Dec 15;132(24):e161408. doi: 10.1172/JCI161408. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 36256480 Free PMC article.
-
Snf1/AMPK fine-tunes TORC1 signaling in response to glucose starvation.Elife. 2023 Feb 7;12:e84319. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84319. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36749016 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

