Therapeutic potential of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists to combat obesity, diabetes, and inflammation
- PMID: 32851581
- PMCID: PMC7572644
- DOI: 10.1007/s11154-020-09584-3
Therapeutic potential of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists to combat obesity, diabetes, and inflammation
Abstract
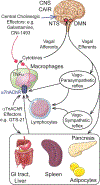
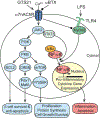
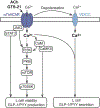
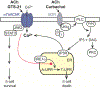
The cholinergic anti-inflammatory reflex (CAIR) represents an important homeostatic regulatory mechanism for sensing and controlling the body's response to inflammatory stimuli. Vagovagal reflexes are an integral component of CAIR whose anti-inflammatory effects are mediated by acetylcholine (ACh) acting at α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (α7nAChR) located on cells of the immune system. Recently, it is appreciated that CAIR and α7nAChR also participate in the control of metabolic homeostasis. This has led to the understanding that defective vagovagal reflex circuitry underlying CAIR might explain the coexistence of obesity, diabetes, and inflammation in the metabolic syndrome. Thus, there is renewed interest in the α7nAChR that mediates CAIR, particularly from the standpoint of therapeutics. Of special note is the recent finding that α7nAChR agonist GTS-21 acts at L-cells of the distal intestine to stimulate the release of two glucoregulatory and anorexigenic hormones: glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY). Furthermore, α7nAChR agonist PNU 282987 exerts trophic factor-like actions to support pancreatic β-cell survival under conditions of stress resembling diabetes. This review provides an overview of α7nAChR function as it pertains to CAIR, vagovagal reflexes, and metabolic homeostasis. We also consider the possible usefulness of α7nAChR agonists for treatment of obesity, diabetes, and inflammation.
Keywords: Cholinergic anti-inflammatory reflex; Diabetes; GLP-1; Obesity; PYY; α7nAChR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit improves energy homeostasis and inhibits inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Metabolism. 2018 Feb;79:52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Metabolism. 2018. PMID: 29129819
-
Alpha-7 Nicotinic Receptor Agonist Protects Mice Against Pulmonary Emphysema Induced by Elastase.Inflammation. 2024 Jun;47(3):958-974. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01953-9. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38227123
-
The Role of α7nAChR-Mediated Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway in Immune Cells.Inflammation. 2021 Jun;44(3):821-834. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01396-6. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33405021 Review.
-
The alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PHA 568487 dampens inflammation in PBMCs from patients with newly discovered coronary artery disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):H1198-H1204. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00562.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39269451
-
Cholinergic modulation of the immune system presents new approaches for treating inflammation.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Nov;179:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28529069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations in Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Various Cognitive Impairments.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Oct;30(10):e70069. doi: 10.1111/cns.70069. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39370620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholinergic dysfunction in COVID-19: frantic search and hoping for the best.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;396(3):453-468. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02346-9. Epub 2022 Dec 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36460816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation as a shared mechanism of chronic stress related disorders with potential novel therapeutic targets.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;397(11):8383-8394. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03205-5. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38850304 Review.
-
Protective effect of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation on experimental colitis and its mechanism.Mol Med. 2022 Sep 4;28(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00532-2. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36058917 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics analysis reveals amelioration effects of yellowhorn tea extract on hyperlipidemia, inflammation, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-fed mice.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 19;10:1087256. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1087256. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36742424 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

