Sphingolipid Metabolism and Signaling in Skeletal Muscle: From Physiology to Physiopathology
- PMID: 32849282
- PMCID: PMC7426366
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00491
Sphingolipid Metabolism and Signaling in Skeletal Muscle: From Physiology to Physiopathology
Abstract
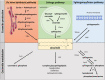
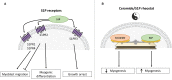
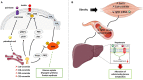
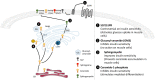
Sphingolipids represent one of the major classes of eukaryotic lipids. They play an essential structural role, especially in cell membranes where they also possess signaling properties and are capable of modulating multiple cell functions, such as apoptosis, cell proliferation, differentiation, and inflammation. Many sphingolipid derivatives, such as ceramide, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and ganglioside, have been shown to play many crucial roles in muscle under physiological and pathological conditions. This review will summarize our knowledge of sphingolipids and their effects on muscle fate, highlighting the role of this class of lipids in modulating muscle cell differentiation, regeneration, aging, response to insulin, and contraction. We show that modulating sphingolipid metabolism may be a novel and interesting way for preventing and/or treating several muscle-related diseases.
Keywords: ceramide; diabetes; glycosphingolipids; insulin; obesity; sphingomyelin; sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Copyright © 2020 Tan-Chen, Guitton, Bourron, Le Stunff and Hajduch.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingolipid metabolism, oxidant signaling, and contractile function of skeletal muscle.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Nov 1;15(9):2501-17. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.3940. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21453197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pleiotropic effects of sphingolipids in skeletal muscle.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Nov;65(23):3725-36. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8236-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18668202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of bioactive sphingolipids in physiology and pathology.Essays Biochem. 2020 Sep 23;64(3):579-589. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190091. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32579188 Review.
-
Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;9(2):139-50. doi: 10.1038/nrm2329. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18216770 Review.
-
Solving the enigma: Mass spectrometry and small molecule probes to study sphingolipid function.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021 Dec;65:49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.05.001. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34175552 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipidomics of infant mesenchymal stem cells associate with the maternal milieu and child adiposity.JCI Insight. 2024 Sep 3;9(19):e180016. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.180016. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39226911 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of let-7 by Electrical Acupuncture Increases Protein Synthesis in Mice.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 20;12:697139. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.697139. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34489723 Free PMC article.
-
The impacts of dietary sphingomyelin supplementation on metabolic parameters of healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Nutr. 2024 Feb 23;11:1363077. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1363077. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38463938 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis revealed potential mechanisms regulating the hypertrophy of goose pectoral muscles.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104498. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104498. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39504833 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of an eight-week high-intensity interval training programme on circulating sphingolipid levels in middle-aged adults at elevated cardiometabolic risk (SphingoFIT)-Protocol for a randomised controlled exercise trial.PLoS One. 2024 May 8;19(5):e0302477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302477. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38717997 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

