Target Analysis and Mechanism of Podophyllotoxin in the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32848800
- PMCID: PMC7427588
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01211
Target Analysis and Mechanism of Podophyllotoxin in the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: As the original compound of many podophyllotoxin derivatives, podophyllotoxin has a beneficial antitumor effect. The mechanism of podophyllotoxin activity in triple-negative breast cancer still needs to be explored.
Methods: We used cell proliferation assay, scratch and transwell experiments, and cell cycle and apoptosis analyses to observe the intervention effect of podophyllotoxin on breast cancer. Furthermore, we analyzed the differences between GSE31448, GSE65194, and GSE45827 in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GEO) and explored the differential genes using a STRING database. Centiscape2.2, MCODE cluster analysis and KEGG pathway analysis were used to identify the most significant gene differences. Next, we utilized BATMAN-TCM and TCMSP databases for further screening to identify key genes. Finally, quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting were performed to detect the expression of key targets.
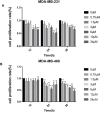
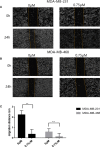
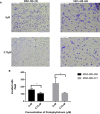
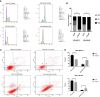
Results: Our research confirmed that podophyllotoxin could not only inhibit the migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer but also affect the cell cycle and induce apoptosis. In total, 566 differential genes were obtained by using the GEO database. After topological network analysis, cluster analysis, and molecular docking screening, we finally identified PLK1, CCDC20, and CDK1 as key target genes. The results of the qRT-PCR assay showed that the mRNA levels of PLK1, CDC20, and CDK1 decreased, while the expression of upstream P53 increased, after drug induction. The Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and conetwork analysis showed that PLK1 is a more critical regulatory factor. Further Western blotting analysis revealed that there was a negative regulatory relationship between the key gene PLK1 and P53 on the protein level. The results were presented as the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate experiments and P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Conclusion: Podophyllotoxin has an intervention effect on the development of triple-negative breast cancer. The expression of PLK1, CDC20, and CDK1 in the cell cycle pathway is inhibited by regulating P53. Our research shows that natural drugs inhibit tumor activity by regulating the expression of cyclins, and the combination of natural drugs and modern extensive database analysis has a wide range of potential applications in the development of antitumor therapies.
Keywords: breast cancer; cell cycle; inhibition; network pharmacology; podophyllotoxin.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Liu, Li, Liu, Zhuang, Feng, Yao and Sun.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifying the Effect of Ursolic Acid Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Coupling Network Pharmacology With Experiments Verification.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 11;12:685773. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.685773. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34858165 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Mechanism of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Cervical Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(8):1547-1559. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230118121436. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 36654467
-
Virtual screening of the multi-gene regulatory molecular mechanism of Si-Wu-tang against non-triple-negative breast cancer based on network pharmacology combined with experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113696. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113696. Epub 2020 Dec 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33358854
-
Identification of Seven Cell Cycle-Related Genes with Unfavorable Prognosis and Construction of their TF-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in Breast Cancer.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(3):740-753. doi: 10.7150/jca.48245. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33403032 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
The network pharmacology study and molecular docking to investigate the potential mechanism of Acoritataninowii Rhizoma against Alzheimer's Disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Aug;38(6):1937-1962. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01179-6. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 37032419
-
Podophyllic Aldehyde, a Podophyllotoxin Derivate, Elicits Different Cell Cycle Profiles Depending on the Tumor Cell Line: A Systematic Proteomic Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 24;25(9):4631. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094631. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731850 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of SSE1806, a Microtubule Destabilizer That Overcomes Multidrug Resistance.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Sep 8;14(10):1369-1377. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00258. eCollection 2023 Oct 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37849542 Free PMC article.
-
Z-Guggulsterone Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Targeting the p53/CCNB1/PLK1 Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.ACS Omega. 2023 Jan 3;8(2):2780-2792. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07480. eCollection 2023 Jan 17. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 36687039 Free PMC article.
-
Plant natural compounds in the cancer treatment: A systematic bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 10;10(14):e34462. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34462. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39104486 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antunez-Mojica M., Rodriguez-Salarichs J., Redondo-Horcajo M., Leon A., Barasoain I., Canales A., et al. (2016). Structural and Biochemical Characterization of the Interaction of Tubulin with Potent Natural Analogues of Podophyllotoxin. J. Nat. Prod. 79 (8), 2113–2121. 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00428 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

