miR-409 and miR-411 Modulation in the Adult Brain of a Rat Model of Depression and After Fluoxetine Treatment
- PMID: 32848656
- PMCID: PMC7427047
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00136
miR-409 and miR-411 Modulation in the Adult Brain of a Rat Model of Depression and After Fluoxetine Treatment
Abstract
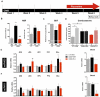
Depression is a chronic debilitating disorder predicted to affect around 20% of the world population. Both brain and peripheral changes, including neuroplastic changes have been shown to occur in the brains of depressed individuals and animal models of depression. Over the past few decades, growing evidence has supported the role of miRNAs as regulators of critical aspects of brain plasticity and function, namely in the context of depression. These molecules are not only highly expressed in the brain, but are also relatively stable in bodily fluids, including blood. Previous microarray analysis from our group has disclosed molecular players in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG), in the context of depression and antidepressant treatment. Two miRNAs in particular-miR-409-5p and miR-411-5p-were significantly up-regulated in the DG of an unpredictable chronic mild stress (CMS) rat model of depression and reversed by antidepressant treatment. Here, we further analyzed the levels of these miRNAs along the DG longitudinal axis and in other brain regions involved in the pathophysiology of depression, as well as in peripheral blood of CMS-exposed rats and after fluoxetine treatment. The effects of CMS and fluoxetine treatment on miR-409-5p and miR-411-5p levels varied across brain regions, and miR-411-5p was significantly decreased in the blood of fluoxetine-treated rats. Additional bioinformatic analyses revealed target genes and pathways of these miRNAs related to neurotransmitter signaling and neuroplasticity functions; an implication of the two miRNAs in the regulation of the cellular and molecular changes observed in these brain regions in depression is worth further examination.
Keywords: chronic stress; depression; fluoxetine; miR-409; miR-411; neural plasticity.
Copyright © 2020 Patrício, Mateus-Pinheiro, Alves, Morais, Rodrigues, Bessa, Sousa and Pinto.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hippocampal miR-211-5p regulates neurogenesis and depression-like behaviors in the rat.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Aug 15;194:108618. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108618. Epub 2021 May 29. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34062164
-
A microarray study of chronic unpredictable mild stress rat blood serum with electro-acupuncture intervention.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Aug 3;627:160-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.05.054. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 27264487
-
miR-30 Family miRNAs Mediate the Effect of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mouse Depression Model.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Aug 8;12:188. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00188. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31440139 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulated miR-192-5p expression rescues cognitive impairment and restores neural function in mice with depression via the Fbln2-mediated TGF-β1 signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2019 Jan;33(1):606-618. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800210RR. Epub 2018 Aug 17. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30118321
-
Dynamic changes of behaviors, dentate gyrus neurogenesis and hippocampal miR-124 expression in rats with depression induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jun;15(6):1150-1159. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.270414. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31823896 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of ncRNAs in depression.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 6;10(6):e27307. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27307. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38496863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers and Predictors of Antidepressant Response in Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Mar 25;16(3):e56910. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56910. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38665721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The important roles of microRNAs in depression: new research progress and future prospects.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 May;99(5):619-636. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02052-8. Epub 2021 Feb 27. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33641067 Review.
-
Beyond New Neurons in the Adult Hippocampus: Imipramine Acts as a Pro-Astrogliogenic Factor and Rescues Cognitive Impairments Induced by Stress Exposure.Cells. 2022 Jan 24;11(3):390. doi: 10.3390/cells11030390. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159199 Free PMC article.
-
Differential microRNA expression in the SH-SY5Y human cell model as potential biomarkers for Huntington's disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jul 10;18:1399742. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1399742. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39049823 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

