Role of Spinal Cord Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathways in Postoperative Hyperalgesia Induced by Plantar Incision in Mice
- PMID: 32848550
- PMCID: PMC7396510
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00766
Role of Spinal Cord Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathways in Postoperative Hyperalgesia Induced by Plantar Incision in Mice
Abstract
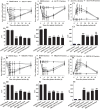
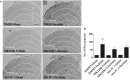
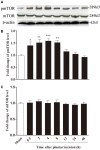
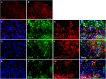
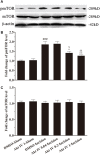
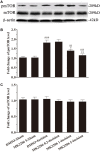
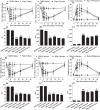
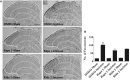
Poor postoperative pain (POP) control increases perioperative morbidity, prolongs hospitalization days, and causes chronic pain. However, the specific mechanism(s) underlying POP is unclear and the identification of optimal perioperative treatment remains elusive. Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) are expressed in the spinal cord, dorsal root ganglion, and sensory axons. In this study, we explored the role of Akt and mTOR in pain-related behaviors induced by plantar incision in mice. Plantar incision activated spinal Akt and mTOR in a dose-dependent manner. Pre-treatment with Akt inhibitors intrathecally prevented the activation of mTOR dose-dependently. In addition, blocking the Akt-mTOR signaling cascade attenuated pain-related behaviors and spinal Fos protein expression induced by plantar incision. Our observations demonstrate that Akt-mTOR might be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of POP.
Keywords: incisional pain; mice; protein kinase B; spinal dorsal corn; the mammalian target of rapamycin kinase.
Copyright © 2020 Xu, Liu, Wei, Jiao, Mo, Lv, Huang, Chen, Ma and Guan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Post-surgical inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase attenuates the plantar incision-induced postoperative pain behavior via spinal Akt activation in male mice.BMC Neurosci. 2019 Jul 31;20(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12868-019-0521-9. BMC Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31366324 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of spinal phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B mediates pain behavior induced by plantar incision in mice.Exp Neurol. 2014 May;255:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.02.019. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24594219
-
CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling mediated ERK1/2 activation in spinal cord contributes to the pathogenesis of postsurgical pain in rats.Mol Pain. 2017 Jan-Dec;13:1744806917718753. doi: 10.1177/1744806917718753. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28633557 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of spinal NF-КB mediates pain behavior induced by plantar incision.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jun 15;8(6):9149-55. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26309571 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing brain mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational regulation: Implications for chronic pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2018 Mar 21;4:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2018.03.002. eCollection 2018 Aug-Dec. Neurobiol Pain. 2018. PMID: 31194026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A prospective cohort study on perioperative percutaneous balloon compression for trigeminal neuralgia: safety and efficacy analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Feb 17;47(1):86. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02323-1. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 38366200
-
Cyclin D1 mediates pain behaviour in a rat model of breast cancer-induced bone pain by a mechanism involving regulation of the proliferation of spinal microglia.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Nov;11(11):803-813. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.1111.BJR-2022-0018.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 36374014 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Incisional Pain: Novel Finding on Long Noncoding RNA XIST/miR-340-5p/RAB1A Axis.ASN Neuro. 2021 Jan-Dec;13:17590914211049056. doi: 10.1177/17590914211049056. ASN Neuro. 2021. PMID: 34806436 Free PMC article.
-
Dezocine relieves the postoperative hyperalgesia in rats through suppressing the hyper-action of Akt1/GSK-3β pathway.Exp Brain Res. 2022 May;240(5):1435-1444. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06341-7. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35333956
-
Activation of Neuroinflammation via mTOR Pathway is Disparately Regulated by Differential Target Multiplexed and Traditional Low-Rate Spinal Cord Stimulation in a Neuropathic Pain Model.J Pain Res. 2022 Sep 13;15:2857-2866. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S378490. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36156899 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

