CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis-Targeted Dual-Functional Nano-Drug Delivery System Against Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 32848392
- PMCID: PMC7426108
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S257527
CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis-Targeted Dual-Functional Nano-Drug Delivery System Against Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Traditional chemotherapy for ovarian cancer is limited due to drug resistance and systemic side effects. Although various targeted drug delivery strategies have been designed to enhance drug accumulation at the tumor site, simply improvement of targeting capability has not consistently led to satisfactory outcomes. Herein, AMD3100 was selected as the targeting ligand because of its high affinity to chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), which was highly expressed on ovarian cancer cells. Moreover, the AMD3100 has been proved having blockage capability of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1 or CXCL12)/CXCR4 axis and to be a sensitizer of chemotherapeutic therapy. We designed a dual-functional targeting delivery system by modifying paclitaxel (PTX)-loaded PEGylation bovine serum albumin (BSA) nanoparticles (NPs) with AMD3100 (AMD-NP-PTX), which can not only achieve specific tumor-targeting efficiency but also enhance the therapeutic outcomes.
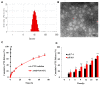
Methods: AMD3100 was chemically modified to Mal-PEG-NHS followed by reacting with BSA, then AMD-NP-PTX was synthesized and characterized. The targeting efficiency of AMD-NP was evaluated both in vitro and in vivo. The anticancer effect of AMD-NP-PTX was determined on Caov3 cells and ovarian cancer-bearing nude mice. Finally, the potential therapeutic mechanism was studied.
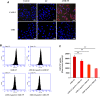
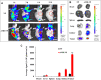
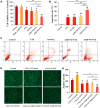
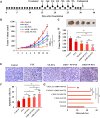
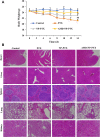
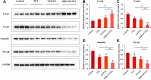
Results: AMD-NP-PTX was synthesized successfully and well characterized. Cellular uptake assay and in vivo imaging experiments demonstrated that NPs could be internalized by Caov3 cells more efficiently after modification of AMD3100. Furthermore, the AMD-NP-PTX exhibited significantly enhanced inhibition effect on tumor growth and metastasis compared with PTX, NP-PTX and free AMD3100 plus NP-PTX both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrated improved safety profile. We also confirmed that AMD-NP-PTX worked through targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 axis, thereby disturbing its downstream signaling pathways including epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) processes and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway.
Conclusion: The AMD-NP-PTX we designed would open a new avenue for dual-functional NPs in ovarian cancer therapy.
Keywords: AMD3100; CXCL12/CXCR4 axis; nanoparticle; ovarian cancer; paclitaxel.
© 2020 Xue et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and evaluation of novel tumor-targeting paclitaxel-loaded nano-carriers for ovarian cancer treatment: in vitro and in vivo.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 26;37(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0700-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29478415 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR7 is not obligatory for CXCL12-CXCR4-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human ovarian cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Jan;58(1):144-155. doi: 10.1002/mc.22916. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 30259564
-
Dual blockade of CXCL12-CXCR4 and PD-1-PD-L1 pathways prolongs survival of ovarian tumor-bearing mice by prevention of immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment.FASEB J. 2019 May;33(5):6596-6608. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802067RR. Epub 2019 Feb 25. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30802149 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in Tumor Immunotherapy.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(17):3026-3041. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170830111531. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 28875842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of CXCL12/CXCR4 axis as a potential targeted therapy of advanced gastric carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2017 Jun;6(6):1424-1436. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1085. Epub 2017 May 23. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28544785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Cancer: from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 26;19(11):3341-3359. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.82317. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37497001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune pathway through endometriosis to ovarian cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 24;15(4):496-522. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.496. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38689629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-Delivery Nanomicelles for Potentiating TNBC Immunotherapy by Synergetically Reshaping CAFs-Mediated Tumor Stroma and Reprogramming Immunosuppressive Microenvironment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jul 31;18:4329-4346. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S418100. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37545872 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Lipid Bilayer Nanocarriers for Cancer Immunotherapy in Heterogeneous Tumor Microenvironments, Combining Immunogenic Cell Death Stimuli with Immune Modulatory Drugs.ACS Nano. 2022 Apr 26;16(4):5184-5232. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c01252. Epub 2022 Mar 29. ACS Nano. 2022. PMID: 35348320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Perspectives of HIV-Associated Chemokine Receptor (CCR5 and CXCR4) Antagonists in Carcinomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 28;24(1):478. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010478. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

