Be aware of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with COVID-19
- PMID: 32844290
- PMCID: PMC7447530
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-020-04715-z
Be aware of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication of critically ill adult patients with COVID-19. However, currently, no studies investigate kidney impairment in children with COVID-19. We investigated incidence and treatment of AKI in pediatric patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan Children's Hospital during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic and discuss possible mechanisms of AKI related to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Methods: By extracting data from electronic medical records, we conducted a retrospective observational study of kidney involvement in confirmed pediatric COVID-19 cases in Wuhan Children's Hospital during the coronavirus outbreak, from January 24 to March 20, 2020. Clinical presentations, clinical courses, laboratory findings, and medical interventions are described below.
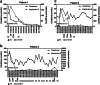
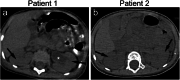
Results: Among 238 confirmed COVID-19 cases, only three were critically ill and needed intensive care unit (ICU) admission. All three developed AKI, but AKI was not detected in any non-critically ill patients outside the ICU. Two of the three patients with AKI had prodromal gastrointestinal symptoms. Significantly elevated interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels and complement activation were observed in these patients with AKI. The three patients with AKI were treated with plasma exchange (PE) and continuous kidney replacement therapy (CKRT), resulting in one complete recovery, one partial recovery, and one mortality due to critical illness.
Conclusions: Critically ill children with COVID-19 may develop AKI, especially following prodromal gastrointestinal symptoms. An inflammatory storm and complement-mediated injury may underlie AKI development in children with COVID-19. Our study supports implantation of PE and CKRT in management of critically ill patients with AKI.
Keywords: AKI; CKRT; COVID-19; Plasmapheresis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical characteristics and outcome of critically ill COVID-19 patients with acute kidney injury: a single centre cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Mar 15;22(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02296-z. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33722189 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Risk Factors and Outcomes: A Single-Center Experience in Brazil.Blood Purif. 2021;50(4-5):520-530. doi: 10.1159/000513425. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Blood Purif. 2021. PMID: 33341806 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021 Jan-Feb;32(1):84-91. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.318551. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021. PMID: 34145117
-
[An overview on acute kidney injury in COVID-19].G Ital Nefrol. 2021 Jun 24;38(3):2021-vol3. G Ital Nefrol. 2021. PMID: 34169691 Review. Italian.
-
Renal replacement therapy for critically ill patients with COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A review of current knowledge.Ther Apher Dial. 2022 Feb;26(1):15-23. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.13723. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Ther Apher Dial. 2022. PMID: 34378870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Children with COVID19.J Trop Pediatr. 2021 May 17;67(2):fmab037. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmab037. J Trop Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34080011 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Tubular Dysfunction Using Urine Biomarkers in Children with COVID-19.Turk Arch Pediatr. 2022 Jan;57(1):99-103. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2022.21248. Turk Arch Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35110086 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Severe Rhabdomyolysis Causing Acute Kidney Injury and Life-Threatening Hyperkalemia in a Pediatric Patient: a Case Report.SN Compr Clin Med. 2023;5(1):121. doi: 10.1007/s42399-023-01453-9. Epub 2023 Apr 12. SN Compr Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37073177 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury outcomes in covid-19 patients: systematic review and meta-analysis.J Bras Nefrol. 2022 Oct-Dec;44(4):543-556. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2022-0013en. J Bras Nefrol. 2022. PMID: 35848725 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jun 15;9:668033. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.668033. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34211943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Z, Wu M, Yao J, Guo J, Liao X, Song S, Li J, Duan G, Zhou Y, Wu X, Zhou Z, Wang T, Hu M, Chen X, Fu Y, Lei C, Dong H, Xu C, Hu Y, Han M, Zhou Y, Jia H, Chen X, Yan J (2020) Caution on kidney dysfunctions of COVID-19 patients. medRxiv. 10.1101/2020.02.08.20021212%JmedRxiv
-
- Diao B, Wang C, Wang R, Feng Z, Tan Y, Wang H, Wang C, Liu L, Liu Y, Liu Y, Wang G, Yuan Z, Ren L, Wu Y, Chen Y (2020) Human kidney is a target for novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. medRxiv, 10.1101/2020.03.04.20031120medRxiv - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2016CFC728/Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province/International
- WX16A07/Key Projects of Scientific Research Program of Wuhan Health Commission me (CN)/International
- WJ2019M011/Healthy Commission of Hubei Province/International
- WHCDCIRB-K-2020007/Centers For Disease Control And Prevention of Wuhan/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

