TIP60 K430 SUMOylation attenuates its interaction with DNA-PKcs in S-phase cells: Facilitating homologous recombination and emerging target for cancer therapy
- PMID: 32832608
- PMCID: PMC7439314
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba7822
TIP60 K430 SUMOylation attenuates its interaction with DNA-PKcs in S-phase cells: Facilitating homologous recombination and emerging target for cancer therapy
Abstract
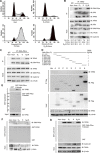
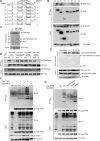
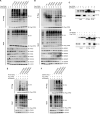
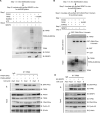
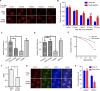
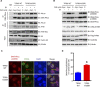
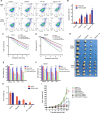
Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) are major repair pathways of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The pathway choice of HR and NHEJ is tightly regulated in cellular response to DNA damage. Here, we demonstrate that the interaction of TIP60 with DNA-PKcs is attenuated specifically in S phase, which facilitates HR pathway activation. SUMO2 modification of TIP60 K430 mediated by PISA4 E3 ligase blocks its interaction with DNA-PKcs, whereas TIP60 K430R mutation recovers its interaction with DNA-PKcs, which results in abnormally increased phosphorylation of DNA-PKcs S2056 in S phase and marked inhibition of HR efficiency, but barely affects NHEJ activity. TIP60 K430R mutant cancer cells are more sensitive to radiation and PARP inhibitors in cancer cell killing and tumor growth inhibition. Collectively, coordinated regulation of TIP60 and DNA-PKcs facilitates HR pathway choice in S-phase cells. TIP60 K430R mutant is a potential target of radiation and PARPi cancer therapy.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of chromatid-break-repair detects a homologous recombination to non-homologous end-joining switch with increasing load of DNA double-strand breaks.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2021 Jul;867:503372. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2021.503372. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2021. PMID: 34266628
-
DNA-PKcs-dependent phosphorylation of RECQL4 promotes NHEJ by stabilizing the NHEJ machinery at DNA double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jun 10;50(10):5635-5651. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac375. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35580045 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nonhomologous DNA end joining, conservative homologous recombination, and single-strand annealing in the cell cycle-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by H(2)O(2) in mammalian cells.Radiat Res. 2008 Dec;170(6):784-93. doi: 10.1667/RR1375.1. Radiat Res. 2008. PMID: 19138034
-
One end to rule them all: Non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks.Br J Radiol. 2020 Nov 1;93(1115):20191054. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20191054. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32105514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice.Cell Res. 2008 Jan;18(1):134-47. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.111. Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18157161 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for keratin 17 during DNA damage response and tumor initiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 30;118(13):e2020150118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2020150118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33762306 Free PMC article.
-
SENP3-mediated TIP60 deSUMOylation is required for DNA-PKcs activity and DNA damage repair.MedComm (2020). 2022 Mar 22;3(2):e123. doi: 10.1002/mco2.123. eCollection 2022 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35356800 Free PMC article.
-
PPIP5K2 promotes colorectal carcinoma pathogenesis through facilitating DNA homologous recombination repair.Oncogene. 2021 Dec;40(49):6680-6691. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02052-5. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34645979
-
Paradoxes of Cellular SUMOylation Regulation: A Role of Biomolecular Condensates?Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Sep;75(5):979-1006. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000784. Epub 2023 May 3. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37137717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPK/FOXO3a Pathway Increases Activity and/or Expression of ATM, DNA-PKcs, Src, EGFR, PDK1, and SOD2 and Induces Radioresistance under Nutrient Starvation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 15;24(16):12828. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612828. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Downs J. A., Jackson S. P., A means to a DNA end: The many roles of Ku. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 367–378 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

