Performance of Non-invasive Blood Parameters for Ruling Out Significant Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 32832394
- PMCID: PMC7438358
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00002
Performance of Non-invasive Blood Parameters for Ruling Out Significant Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
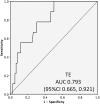
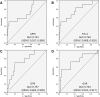
Background and Aims: Evaluation of significant liver fibrosis is important for treatment decision and treatment response evaluation in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Since liver biopsy is invasive and transient elastography (TE) has limited availability, various non-invasive blood parameters need evaluation for their capabilities for detection of significant fibrosis. Methods: In this retrospective study, records of patients who had undergone liver biopsy for treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B were evaluated to obtain various non-invasive blood parameters (aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index [referred to as APRI], Fibrosis-4 score [referred to as FIB-4], gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio [referred to as GPR], and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-albumin ratio [referred to as GAR]), in addition to TE, to assess significant liver fibrosis and compare these to fibrosis stage in liver biopsy. Results: A total of 113 patients were included in the study (median age 33 [interquartile range: 11-82 years], 74% males). Most (75%) patients were HBeAg-negative. The liver biopsy revealed significant fibrosis (Ishak ≥3) in 13% of the patients and nil or mild fibrosis (Ishak <3) in 87% of the patients. TE findings were available for 85 patients, APRI and FIB-4 for 95 patients, GPR for 79 patients, and GAR for 78 patients. The median values of all the parameters were significantly higher in patients with significant fibrosis, as compared to patients with non-significant fibrosis, and all the blood parameters as well as TE were able to identify patients with significant fibrosis significantly well (p<0.05). All non-invasive parameters had low positive predictive value but negative predictive value above 92%. Compared to TE, all the non-invasive blood parameters had similar area under the curve for detecting significant fibrosis, with excellent negative predictive value (≥93%). Conclusions: Non-invasive blood parameters (APRI, FIB-4, GPR, and GAR) with negative predictive values above 93% are excellent parameters for ruling-out significant fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. These can be used at bedside in place of TE.
Keywords: APRI; Cirrhosis; FIB-4; GAR; GPR; Hepatitis B; Liver fibrosis; Transient elastography.
© 2020 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio can reduce the need for transient elastography in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(49):e18038. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018038. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31804310 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of GPR versus APRI and FIB-4 in predicting different levels of liver fibrosis of chronic hepatitis B.J Viral Hepat. 2018 May;25(5):581-589. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12842. Epub 2018 Jan 4. J Viral Hepat. 2018. PMID: 29230907
-
Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase-to-Platelet ratio predicts liver fibrosis in patients with concomitant chronic hepatitis B and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Aug;36(8):e24596. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24596. Epub 2022 Jul 9. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35808928 Free PMC article.
-
The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio predicts liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in HBeAg-positive chronic HBV infection patients with high HBV DNA and normal or mildly elevated alanine transaminase levels in China.J Viral Hepat. 2016 Nov;23(11):912-919. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12563. Epub 2016 Jul 4. J Viral Hepat. 2016. PMID: 27375134
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: direct comparisons of biomarkers for the diagnosis of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C and B.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Jan;43(1):16-29. doi: 10.1111/apt.13446. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26516104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comparative Analysis of the APRI, FIB4, and FibroScan Score in Evaluating the Severity of Chronic Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients in India.Cureus. 2021 Nov 7;13(11):e19342. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19342. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34909303 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of GPR score for non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B Tunisian patients.Tunis Med. 2024 Oct 5;102(10):715-721. doi: 10.62438/tunismed.v102i10.5091. Tunis Med. 2024. PMID: 39441156 Free PMC article. French.
-
Nomogram for evaluating obvious liver inflammation in treatment-naïve HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection patients with normal ALT.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2158710. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2158710. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 36600180 Free PMC article.
-
Serum CHI3L1 as a diagnostic marker and risk factor for liver fibrosis in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jun 15;14(6):4090-4096. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35836859 Free PMC article.
-
Improving care of migrants is key for viral hepatitis elimination in Europe.Bull World Health Organ. 2021 Apr 1;99(4):280-286. doi: 10.2471/BLT.20.260919. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Bull World Health Organ. 2021. PMID: 33953445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Background-epidemiology and natural history. In: WHO. guidelines on hepatitis B and C testing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442290/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
