Caveolin-3: A Causative Process of Chicken Muscular Dystrophy
- PMID: 32825241
- PMCID: PMC7565761
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10091206
Caveolin-3: A Causative Process of Chicken Muscular Dystrophy
Abstract
The etiology of chicken muscular dystrophy is the synthesis of aberrant WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 1 (WWP1) protein made by a missense mutation of WWP1 gene. The β-dystroglycan that confers stability to sarcolemma was identified as a substrate of WWP protein, which induces the next molecular collapse. The aberrant WWP1 increases the ubiquitin ligase-mediated ubiquitination following severe degradation of sarcolemmal and cytoplasmic β-dystroglycan, and an erased β-dystroglycan in dystrophic αW fibers will lead to molecular imperfection of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC). The DGC is a core protein of costamere that is an essential part of force transduction and protects the muscle fibers from contraction-induced damage. Caveolin-3 (Cav-3) and dystrophin bind competitively to the same site of β-dystroglycan, and excessive Cav-3 on sarcolemma will block the interaction of dystrophin with β-dystroglycan, which is another reason for the disruption of the DGC. It is known that fast-twitch glycolytic fibers are more sensitive and vulnerable to contraction-induced small tears than slow-twitch oxidative fibers under a variety of diseased conditions. Accordingly, the fast glycolytic αW fibers must be easy with rapid damage of sarcolemma corruption seen in chicken muscular dystrophy, but the slow oxidative fibers are able to escape from these damages.
Keywords: Caveolin-3; WWP1; chicken muscular dystrophy; stretching; β-dystroglycan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
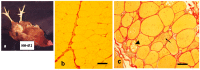
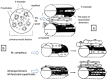
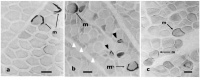

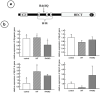
Similar articles
-
β-dystroglycan is regulated by a balance between WWP1-mediated degradation and protection from WWP1 by dystrophin and utrophin.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Jun;1864(6 Pt A):2199-2213. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29635000
-
Characterization of WWP1 protein expression in skeletal muscle of muscular dystrophy chickens.J Biochem. 2016 Feb;159(2):171-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvv084. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26314333 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-3 directly interacts with the C-terminal tail of beta -dystroglycan. Identification of a central WW-like domain within caveolin family members.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 1;275(48):38048-58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005321200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10988290
-
Dystroglycan and muscular dystrophies related to the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex.Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2003;39(2):173-81. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2003. PMID: 14587215 Review.
-
Caveolin and NOS in the Development of Muscular Dystrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 12;25(16):8771. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168771. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional profiling of the M. complexus in naked neck chickens suggest a direct pleiotropic effect of GDF7 on feathering and reduced hatchability.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 15;25(1):1092. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10965-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39548399 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prognostic hub genes and therapeutic targets for selenium deficiency in chicks model through transcriptome profiling.Sci Rep. 2023 May 29;13(1):8695. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34955-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37248251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asmundson V.S., Julian L.M. Inherited muscle abnormality in the domestic fowl. J. Hered. 1956;47:248–252. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106655. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

