Merged Tacrine-Based, Multitarget-Directed Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors 2015-Present: Synthesis and Biological Activity
- PMID: 32825138
- PMCID: PMC7504404
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21175965
Merged Tacrine-Based, Multitarget-Directed Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors 2015-Present: Synthesis and Biological Activity
Abstract
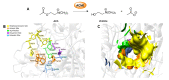
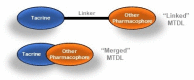
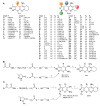
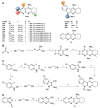
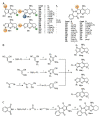
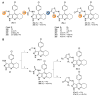
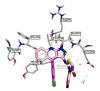
Acetylcholinesterase is an important biochemical enzyme in that it controls acetylcholine-mediated neuronal transmission in the central nervous system, contains a unique structure with two binding sites connected by a gorge region, and it has historically been the main pharmacological target for treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Given the large projected increase in Alzheimer's disease cases in the coming decades and its complex, multifactorial nature, new drugs that target multiple aspects of the disease at once are needed. Tacrine, the first acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used clinically but withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity concerns, remains an important starting point in research for the development of multitarget-directed acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. This review highlights tacrine-based, multitarget-directed acetylcholinesterase inhibitors published in the literature since 2015 with a specific focus on merged compounds (i.e., compounds where tacrine and a second pharmacophore show significant overlap in structure). The synthesis of these compounds from readily available starting materials is discussed, along with acetylcholinesterase inhibition data, relative to tacrine, and structure activity relationships. Where applicable, molecular modeling, to elucidate key enzyme-inhibitor interactions, and secondary biological activity is highlighted. Of the numerous compounds identified, there is a subset with promising preliminary screening results, which should inspire further development and future research in this field.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Friedländer reaction; acetylcholinesterase; multitarget-directed ligand; pyranopyrazole; tacrine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
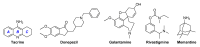

Similar articles
-
Tacrines as Therapeutic Agents for Alzheimer's Disease. V. Recent Developments.Chem Rec. 2021 Jan;21(1):162-174. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202000107. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Chem Rec. 2021. PMID: 33169934 Review.
-
Tacrine-O-protected phenolics heterodimers as multitarget-directed ligands against Alzheimer's disease: Selective subnanomolar BuChE inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 1;181:111550. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.07.053. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31376562
-
Synthesis and biological assessment of KojoTacrines as new agents for Alzheimer's disease therapy.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):163-170. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1538136. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30482062 Free PMC article.
-
A novel class of multitarget anti-Alzheimer benzohomoadamantane‒chlorotacrine hybrids modulating cholinesterases and glutamate NMDA receptors.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 15;180:613-626. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.07.051. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31351393
-
Tacrine-based Multifunctional Agents in Alzheimer's Disease: An Old Story in Continuous Development§.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(32):3522-3546. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170309123920. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28294041 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory Activity of 4-Benzylidene Oxazolones Derivatives of Cinnamic Acid on Human Acetylcholinesterase and Cognitive Improvements in a Mouse Model.Molecules. 2023 Nov 2;28(21):7392. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217392. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959813 Free PMC article.
-
A Smartphone Camera Colorimetric Assay of Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Activity.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;21(5):1796. doi: 10.3390/s21051796. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807562 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis and Bioactivity Evaluation of Coumarin-BMT Hybrids as New Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2022 Mar 26;27(7):2142. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072142. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408542 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Linkers and Substitutions on Multitarget Directed Ligands for Alzheimer's Diseases: Emerging Paradigms and Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 29;23(11):6085. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116085. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hepatoprotective effect of 4-phenyltetrahydroquinolines on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in rats through autophagy inhibition.Biol Res. 2024 May 27;57(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00510-4. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38797855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quinn D.M. Acetylcholinesterase: Enzyme structure, reaction dynamics, and virtual transition states. Chem. Rev. 1987;87:955–979. doi: 10.1021/cr00081a005. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

