Association of Electronegative LDL with Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and CD11c Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
- PMID: 32824307
- PMCID: PMC7461586
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21165883
Association of Electronegative LDL with Macrophage Foam Cell Formation and CD11c Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
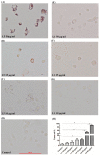
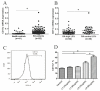
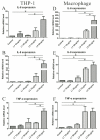
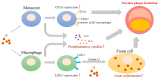
L5, the most negatively charged subfraction of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), is implicated in atherogenesis, but the pathogenic association is relatively unexplored in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We examined the role of L5 LDL in macrophage foam cell formation and the association of L5 with CD11c expression in THP-1 cells and RA patients. Using quantitative real-time PCR, we determined mRNA expression levels of ITGAX, the gene for CD11c, a marker associated with vascular plaque formation and M1 macrophages in atherogenesis, in 93 RA patients. We also examined CD11c expression on THP-1 cells treated with L5 by flow cytometry analysis and the plasma levels of inflammatory mediators using a magnetic bead array. We found a dose-dependent upregulation of foam cell formation of macrophages after L5 treatment (mean ± SEM, 12.05 ± 2.35% in L5 (10 µg/mL); 50.13 ± 3.9% in L5 (25 µg/mL); 90.69 ± 1.82% in L5 (50 µg/mL), p < 0.01). Significantly higher levels of CD11c expression were observed in 30 patients with a high percentage of L5 in LDL (L5%) (0.0752 ± 0.0139-fold) compared to 63 patients with normal L5% (0.0446 ± 0.0054-fold, p < 0.05). CD11c expression levels were increased in the L5-treated group (30.00 ± 3.13% in L5 (10 µg/mL); 41.46 ± 2.77% in L5 (50 µg/mL), p < 0.05) and were positively correlated with plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8. L5 augmented the expression of IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) on monocytes and macrophages. Our findings suggest that L5 may promote atherogenesis by augmenting macrophage foam cell formation, upregulating CD11c expression, and enhancing the expression levels of atherosclerosis-related mediators.
Keywords: CD11c expression; L5; atherosclerosis; macrophage foam cell; rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Potential Role of Electronegative High-Density Lipoprotein H5 Subfraction in RA-Related Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 22;22(21):11419. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111419. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768851 Free PMC article.
-
Curcuma oil attenuates accelerated atherosclerosis and macrophage foam-cell formation by modulating genes involved in plaque stability, lipid homeostasis and inflammation.Br J Nutr. 2015 Jan 14;113(1):100-13. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514003195. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Br J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25391643
-
Electronegative Low-Density Lipoprotein L5 Induces Adipose Tissue Inflammation Associated With Metabolic Syndrome.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Dec 1;102(12):4615-4625. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01657. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29029093
-
Macrophage foam cell formation during early atherogenesis is determined by the balance between pro-oxidants and anti-oxidants in arterial cells and blood lipoproteins.Antioxid Redox Signal. 1999 Winter;1(4):585-94. doi: 10.1089/ars.1999.1.4-585. Antioxid Redox Signal. 1999. PMID: 11233155 Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein modified by myeloperoxidase in inflammatory pathways and clinical studies.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:971579. doi: 10.1155/2013/971579. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23983406 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The NLRP3 Inflammasome as a Pathogenic Player Showing Therapeutic Potential in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Comorbidities: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 3;25(1):626. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010626. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: An Update on the Role of Atherogenic Electronegative LDL and Potential Therapeutic Strategies.J Clin Med. 2021 May 6;10(9):1992. doi: 10.3390/jcm10091992. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34066436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Extraarticular Manifestations in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 24;11(5):1262. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051262. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified Lipoproteins Induce Arterial Wall Inflammation During Atherogenesis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Mar 3;9:841545. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.841545. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35310965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oxidized Lipoproteins In Vivo: Its Diversity and Behavior in the Human Circulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5747. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065747. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cvetkovic J.T., Wallberg-Jonsson S., Ahmed E., Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S., Lefvert A.K. Increased levels of autoantibodies against copper-oxidized low density lipoprotein, malondialdehyde-modified low density lipoprotein and cardiolipin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2002;41:988–995. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.9.988. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

