Annexin A1: A Bane or a Boon in Cancer? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32823805
- PMCID: PMC7465196
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25163700
Annexin A1: A Bane or a Boon in Cancer? A Systematic Review
Abstract
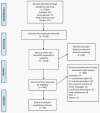
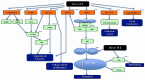
Annexin A1 has been extensively investigated as an anti-inflammatory protein, but its role in different types of cancer has not been consolidated in a single systematic review to date. Thus, the aim of this paper is to systematically review and critically analyse 18 studies (in-vivo and in-vitro) to consolidate, in a concerted manner, all the information on differential expression of Annexin A1 in different types of cancer and the role this protein plays in tumorigenesis. Pubmed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect were used for the literature search and the keywords used are "annexin A1," "lipocortin 1," "cancer," "malignancy," "neoplasm," "neoplasia," and "tumor." A total of 1128 articles were retrieved by implementing a standard search strategy subjected to meticulous screening processes and 442 articles were selected for full article screening. A total of 18 articles that adhered to the inclusion criteria were included in the systematic review and these articles possessed low to moderate bias. These studies showed a strong correlation between Annexin A1 expression and cancer progression via modulation of various cancer-associated pathways. Differential expression of Annexin A1 is shown to play a role in cellular proliferation, metastasis, lymphatic invasion, and development of resistance to anti-cancer treatment. Meta-analysis in the future may provide a statistically driven association between Annexin A1 expression and malignancy progression.
Keywords: Annexin A1; cancer; gene expression; lipocortin 1; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Annexin-A1 - A Blessing or a Curse in Cancer?Trends Mol Med. 2019 Apr;25(4):315-327. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Trends Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30871809 Review.
-
Annexin A1 in malignant tumors: current opinions and controversies.Int J Biol Markers. 2014 Mar 24;29(1):e8-20. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000046. Int J Biol Markers. 2014. PMID: 24242295 Review.
-
Annexin A1 expression is correlated with malignant potential of renal cell carcinoma.Int J Urol. 2019 Feb;26(2):284-290. doi: 10.1111/iju.13869. Epub 2018 Dec 2. Int J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30506742
-
Annexin A1 as a Regulator of Immune Response in Cancer.Cells. 2021 Aug 30;10(9):2245. doi: 10.3390/cells10092245. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annexin A1 is involved in the acquisition and maintenance of a stem cell-like/aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer cells with acquired resistance to zoledronic acid.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):25076-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4725. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26312765 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomics Reveals mRNA Regulation and the Action of Annexins in Thyroid Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 26;24(19):14542. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914542. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833989 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profiles of GILZ and Annexin A1 in Human Oral Candidiasis and Lichen Planus.Cells. 2022 Apr 27;11(9):1470. doi: 10.3390/cells11091470. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563776 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted proteomics-derived biomarker profile develops a multi-protein classifier in liquid biopsies for early detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from a population-based case-control study.Biomark Res. 2021 Feb 17;9(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00266-z. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 33597040 Free PMC article.
-
Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-α/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation.Open Life Sci. 2022 Mar 18;17(1):208-220. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0023. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35415239 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of cell death and modulation of Annexin A1 by phytoestrogens in human leukemic cell lines.Saudi Pharm J. 2021 Jan;29(1):73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.12.011. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Saudi Pharm J. 2021. PMID: 33603542 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources