Helicobacter pylori infection: Beyond gastric manifestations
- PMID: 32821071
- PMCID: PMC7403793
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4076
Helicobacter pylori infection: Beyond gastric manifestations
Abstract
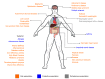
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium that infects more than a half of world's population. Although it is mainly related to the development of gastroduodenal diseases, several studies have shown that such infection may also influence the development and severity of various extragastric diseases. According to the current evidence, whereas this bacterium is a risk factor for some of these manifestations, it might play a protective role in other pathological conditions. In that context, when considered the gastrointestinal tract, H. pylori positivity have been related to Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Hepatic Carcinoma, Cholelithiasis, and Cholecystitis. Moreover, lower serum levels of iron and vitamin B12 have been found in patients with H. pylori infection, leading to the emergence of anemias in a portion of them. With regards to neurological manifestations, a growing number of studies have associated that bacterium with multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Interestingly, the risk of developing cardiovascular disorders, such as atherosclerosis, is also influenced by the infection. Besides that, the H. pylori-associated inflammation may also lead to increased insulin resistance, leading to a higher risk of diabetes mellitus among infected individuals. Finally, the occurrence of dermatological and ophthalmic disorders have also been related to that microorganism. In this sense, this minireview aims to gather the main studies associating H. pylori infection with extragastric conditions, and also to explore the main mechanisms that may explain the role of H. pylori in those diseases.
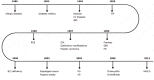
Keywords: Autoimmune; Cardiovascular; Diabetes; Extragastric; Helicobacter pylori; Neurological; Ophthalmic; Timeline; Treatment.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no conflict of interest associated with any of the senior author or other coauthors contributed their efforts in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori Infection and Extragastric Diseases-A Focus on the Central Nervous System.Cells. 2021 Aug 25;10(9):2191. doi: 10.3390/cells10092191. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: Possible role of bacterium in liver and pancreas diseases.World J Hepatol. 2015 Dec 28;7(30):2968-79. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i30.2968. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26730276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on Helicobacter pylori infection related neurological diseases.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Aug;99:102399. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102399. Epub 2024 Jun 30. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38955263 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori and extragastric diseases: A review.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 7;24(29):3204-3221. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i29.3204. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30090002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection: a clinical overview.Dig Liver Dis. 2008 Aug;40(8):619-26. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2008.02.026. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Dig Liver Dis. 2008. PMID: 18396114 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiota Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Carcinogenesis through Altered Immune Response.Microorganisms. 2023 May 8;11(5):1240. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051240. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori infection exacerbates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through lipid metabolic pathways: a transcriptomic study.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 29;22(1):701. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05506-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39075482 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between H. pylori Infection and Colorectal Polyps: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 18;8:706036. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.706036. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35118081 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerating action to reduce anemia: Review of causes and risk factors and related data needs.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2023 May;1523(1):11-23. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14985. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2023. PMID: 36987993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric microbiota dysbiosis and Helicobacter pylori infection.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1153269. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1153269. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37065152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coelho LGV, Marinho JR, Genta R, Ribeiro LT, Passos MDCF, Zaterka S, Assumpção PP, Barbosa AJA, Barbuti R, Braga LL, Breyer H, Carvalhaes A, Chinzon D, Cury M, Domingues G, Jorge JL, Maguilnik I, Marinho FP, Moraes-Filho JP, Parente JML, Paula-E-Silva CM, Pedrazzoli-Júnior J, Ramos AFP, Seidler H, Spinelli JN, Zir JV. Ivth brazilian consensus conference on Helicobacter pylori infection. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018;55:97–121. - PubMed
-
- Sjomina O, Pavlova J, Niv Y, Leja M. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2018;23 Suppl 1:e12514. - PubMed
-
- Leja M, Grinberga-Derica I, Bilgilier C, Steininger C. Review: Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2019;24 Suppl 1:e12635. - PubMed
-
- Urita Y, Watanabe T, Kawagoe N, Takemoto I, Tanaka H, Kijima S, Kido H, Maeda T, Sugasawa Y, Miyazaki T, Honda Y, Nakanishi K, Shimada N, Nakajima H, Sugimoto M, Urita C. Role of infected grandmothers in transmission of Helicobacter pylori to children in a Japanese rural town. J Paediatr Child Health. 2013;49:394–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

