Motto: Representing Motifs in Consensus Sequences with Minimum Information Loss
- PMID: 32816922
- PMCID: PMC7536857
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.120.303597
Motto: Representing Motifs in Consensus Sequences with Minimum Information Loss
Abstract
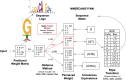
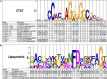
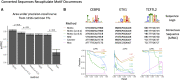
Sequence analysis frequently requires intuitive understanding and convenient representation of motifs. Typically, motifs are represented as position weight matrices (PWMs) and visualized using sequence logos. However, in many scenarios, in order to interpret the motif information or search for motif matches, it is compact and sufficient to represent motifs by wildcard-style consensus sequences (such as [GC][AT]GATAAG[GAC]). Based on mutual information theory and Jensen-Shannon divergence, we propose a mathematical framework to minimize the information loss in converting PWMs to consensus sequences. We name this representation as sequence Motto and have implemented an efficient algorithm with flexible options for converting motif PWMs into Motto from nucleotides, amino acids, and customized characters. We show that this representation provides a simple and efficient way to identify the binding sites of 1156 common transcription factors (TFs) in the human genome. The effectiveness of the method was benchmarked by comparing sequence matches found by Motto with PWM scanning results found by FIMO. On average, our method achieves a 0.81 area under the precision-recall curve, significantly (P-value < 0.01) outperforming all existing methods, including maximal positional weight, Cavener's method, and minimal mean square error. We believe this representation provides a distilled summary of a motif, as well as the statistical justification.
Keywords: consensus; information theory; motif; sequence logo; transcription factor binding.
Copyright © 2020 Wang et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
abc4pwm: affinity based clustering for position weight matrices in applications of DNA sequence analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Mar 3;23(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04615-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35240993 Free PMC article.
-
P-value-based regulatory motif discovery using positional weight matrices.Genome Res. 2013 Jan;23(1):181-94. doi: 10.1101/gr.139881.112. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 22990209 Free PMC article.
-
Metamotifs--a generative model for building families of nucleotide position weight matrices.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun 25;11:348. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-348. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20579334 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Motif Databases and Their Uses.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 3;51:2.15.1-2.15.6. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0215s51. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26334922 Review.
-
Discovering sequence motifs.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;452:231-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-159-2_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18566768 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporally discordant chromatin accessibility and DNA demethylation define short and long-term enhancer regulation during cell fate specification.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 27:2024.08.27.609789. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.27.609789. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253426 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
DNA Transposons Favor De Novo Transcript Emergence Through Enrichment of Transcription Factor Binding Motifs.Genome Biol Evol. 2024 Jul 3;16(7):evae134. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evae134. Genome Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38934893 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of DNA motifs that regulate DNA methylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 26;47(13):6753-6768. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz483. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31334813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey T. L., and Elkan C., 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in bipolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 2: 28–36 - PubMed
-
- Davis, J., and M. Goadrich, 2006 The Relationship Between Precision-Recall and ROC Curves, pp. 233–240 in Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML ’06. ACM, New York. 10.1145/1143844.114387410.1145/1143844.1143874 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

