Role of EGFR in the Nervous System
- PMID: 32806510
- PMCID: PMC7464966
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9081887
Role of EGFR in the Nervous System
Abstract
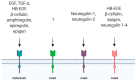
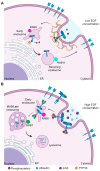
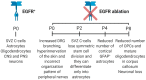
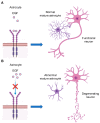
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is the first discovered member of the receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily and plays a fundamental role during embryogenesis and in adult tissues, being involved in growth, differentiation, maintenance and repair of various tissues and organs. The role of EGFR in the regulation of tissue development and homeostasis has been thoroughly investigated and it has also been demonstrated that EGFR is a driver of tumorigenesis. In the nervous system, other growth factors, and thus other receptors, are important for growth, differentiation and repair of the tissue, namely neurotrophins and neurotrophins receptors. For this reason, for a long time, the role of EGFR in the nervous system has been underestimated and poorly investigated. However, EGFR is expressed both in the central and peripheral nervous systems and it has been demonstrated to have specific important neurotrophic functions, in particular in the central nervous system. This review discusses the role of EGFR in regulating differentiation and functions of neurons and neuroglia. Furthermore, its involvement in regeneration after injury and in the onset of neurodegenerative diseases is examined.
Keywords: EGF; EGFR; brain; central nervous system; neurodegenerative disease; neurons; peripheral nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Neuronal growth factors--neurotrophins].Ugeskr Laeger. 1999 Apr 5;161(14):2063-70. Ugeskr Laeger. 1999. PMID: 10354791 Review. Danish.
-
Drug Targets in Neurotrophin Signaling in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Aug;55(8):6939-6955. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0885-3. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29372544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGF family of growth factors: essential roles and functional redundancy in the nerve system.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:85-92. doi: 10.2741/1210. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766347 Review.
-
Peripheral nerve injury modulates neurotrophin signaling in the peripheral and central nervous system.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Dec;50(3):945-70. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8706-9. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24752592 Review.
-
Neurotrophin-3 in the development of the enteric nervous system.Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:243-63. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(03)46016-0. Prog Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14699968 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the pathogenic interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and polycystic ovary syndrome using bioinformatics and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):22934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74347-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39358491 Free PMC article.
-
Competing endogenous RNAs in human astrocytes: crosstalk and interacting networks in response to lipotoxicity.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 13;17:1195840. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1195840. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38027526 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Potential Anti-Alzheimer's Disease Mechanism of Marine Polyphenols: Insights from Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Mar Drugs. 2023 Nov 6;21(11):580. doi: 10.3390/md21110580. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37999404 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of MicroRNA-mRNA Networks in Dorsal Root Ganglia after Peripheral Nerve Injury.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jul 11;19(8):1275-1289. doi: 10.7150/ijms.73113. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35928719 Free PMC article.
-
c-Cbl Regulates Murine Subventricular Zone-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells in Dependence of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor.Cells. 2023 Oct 3;12(19):2400. doi: 10.3390/cells12192400. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830613 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

