Therapeutic Trem2 activation ameliorates amyloid-beta deposition and improves cognition in the 5XFAD model of amyloid deposition
- PMID: 32795308
- PMCID: PMC7427742
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-020-01915-0
Therapeutic Trem2 activation ameliorates amyloid-beta deposition and improves cognition in the 5XFAD model of amyloid deposition
Abstract
Background: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell-2 (TREM2) is a lipid and lipoprotein binding receptor expressed by cells of myeloid origin. Homozygous TREM2 mutations cause early onset progressive presenile dementia while heterozygous, point mutations triple the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although human genetic findings support the notion that loss of TREM2 function exacerbates neurodegeneration, it is not clear whether activation of TREM2 in a disease state would result in therapeutic benefits. To determine the viability of TREM2 activation as a therapeutic strategy, we sought to characterize an agonistic Trem2 antibody (AL002a) and test its efficacy and mechanism of action in an aggressive mouse model of amyloid deposition.
Methods: To determine whether agonism of Trem2 results in therapeutic benefits, we designed both intracranial and systemic administration studies. 5XFAD mice in the intracranial administration study were assigned to one of two injection groups: AL002a, a Trem2-agonizing antibody, or MOPC, an isotype-matched control antibody. Mice were then subject to a single bilateral intracranial injection into the frontal cortex and hippocampus and euthanized 72 h later. The tissue from the left hemisphere was histologically examined for amyloid-beta and microglia activation, whereas the tissue from the right hemisphere was used for biochemical analyses. Similarly, mice in the systemic administration study were randomized to one of the aforementioned injection groups and the assigned antibody was administered intraperitoneally once a week for 14 weeks. Mice underwent behavioral assessment between the 12- and 14-week timepoints and were euthanized 24 h after their final injection. The tissue from the left hemisphere was used for histological analyses whereas the tissue from the right hemisphere was used for biochemical analyses.
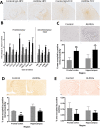
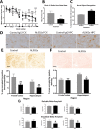
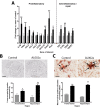
Results: Here, we show that chronic activation of Trem2, in the 5XFAD mouse model of amyloid deposition, leads to reversal of the amyloid-associated gene expression signature, recruitment of microglia to plaques, decreased amyloid deposition, and improvement in spatial learning and novel object recognition memory.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that Trem2 activators may be effective for the treatment of AD and possibly other neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Beta-amyloid; Immuno-neurology; Immunotherapy; Neuroinflammation; TREM2; Trem2.
Conflict of interest statement
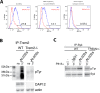
Dr. Wilcock has been a paid consultant of Alector. Data for Fig. 1 were generated by scientists at Alector.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prior activation state shapes the microglia response to antihuman TREM2 in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 19;118(3):e2017742118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2017742118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33446504 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of amyloid on microglia-neuron interactions before plaque onset occurs independently of TREM2 in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Nov;145:105072. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105072. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32890775 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and engineering of an anti-TREM2 antibody to promote amyloid plaque clearance by microglia in 5XFAD mice.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2107971. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2107971. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 35921534 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of TREM2 in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Dec 20;13(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0298-9. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30572908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TREM2 Function in Alzheimer's Disease and Neurodegeneration.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Apr 20;7(4):420-7. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00313. Epub 2016 Feb 19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26854967 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting TREM2 signaling shows limited impact on cerebrovascular calcification.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Oct 28;8(1):e202402796. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202402796. Print 2025 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 39467636 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic TREM2 activation exacerbates Aβ-associated tau seeding and spreading.J Exp Med. 2023 Jan 2;220(1):e20220654. doi: 10.1084/jem.20220654. Epub 2022 Oct 11. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36219197 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Targets for Small Molecules.Molecules. 2022 Jun 27;27(13):4124. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134124. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T cell adoptive transfer alters uterine immune populations, increasing a novel MHC-IIlow macrophage associated with healthy pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 13;14:1256453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1256453. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37901247 Free PMC article.
-
Trem2 Agonist Reprograms Foamy Macrophages to Promote Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability-Brief Report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Jul;44(7):1646-1657. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320797. Epub 2024 May 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38695172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 2020. - PubMed
-
- Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B: The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2011, 10:698-712. - PubMed
-
- Salloway S, Sperling R, Brashear HR. Phase 3 trials of solanezumab and bapineuzumab for Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1460. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

