Menthol can be safely applied to improve thermal perception during physical exercise: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 32788718
- PMCID: PMC7423903
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-70499-9
Menthol can be safely applied to improve thermal perception during physical exercise: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Menthol is often used as a cold-mimicking substance to allegedly enhance performance during physical activity, however menthol-induced activation of cold-defence responses during exercise can intensify heat accumulation in the body. This meta-analysis aimed at studying the effects of menthol on thermal perception and thermophysiological homeostasis during exercise. PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar databases were searched until May 2020. Menthol caused cooler thermal sensation by weighted mean difference (WMD) of - 1.65 (95% CI, - 2.96 to - 0.33) and tended to improve thermal comfort (WMD = 1.42; 95% CI, - 0.13 to 2.96) during physical exercise. However, there was no meaningful difference in sweat production (WMD = - 24.10 ml; 95% CI, - 139.59 to 91.39 ml), deep body temperature (WMD = 0.02 °C; 95% CI, - 0.11 to 0.15 °C), and heart rate (WMD = 2.67 bpm; 95% CI - 0.74 to 6.09 bpm) between the treatment groups. Menthol improved the performance time in certain subgroups, which are discussed. Our findings suggest that different factors, viz., external application, warmer environment, and higher body mass index can improve menthol's effects on endurance performance, however menthol does not compromise warmth-defence responses during exercise, thus it can be safely applied by athletes from the thermoregulation point of view.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
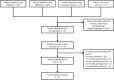






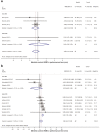
Similar articles
-
Thermo-behavioural responses to orally applied l-menthol exhibit sex-specific differences during exercise in a hot environment.Physiol Behav. 2021 Feb 1;229:113250. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113250. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Physiol Behav. 2021. PMID: 33220326 Clinical Trial.
-
The influence of menthol dose on human temperature regulation and perception.J Therm Biol. 2020 Aug;92:102659. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2020.102659. Epub 2020 Aug 1. J Therm Biol. 2020. PMID: 32888563
-
Topical application of isolated menthol and combined menthol-capsaicin creams: Exercise tolerance, thermal perception, pain, attentional focus and thermoregulation in the heat.Eur J Sport Sci. 2023 Oct;23(10):2038-2048. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2023.2211966. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023. PMID: 37161852 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of menthol on exercise performance and thermal sensation: A meta-analysis.J Sci Med Sport. 2019 Jun;22(6):707-715. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 6. J Sci Med Sport. 2019. PMID: 30554924 Review.
-
Menthol Use for Performance in Hot Environments.Curr Sports Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):135-139. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000474. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29629974 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance effects of internal pre- and per-cooling across different exercise and environmental conditions: A systematic review.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 14;9:959516. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.959516. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36337635 Free PMC article.
-
Cumulative pre-cooling methods do not enhance cycling performance in tropical climate.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 12;18(10):e0291951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291951. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37824451 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sepsis: meta-analysis of clinical trials.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 13;11(1):8051. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87613-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33850259 Free PMC article.
-
Temperate Air Breathing Increases Cycling Performance in Hot and Humid Climate Environment.Life (Basel). 2021 Sep 1;11(9):911. doi: 10.3390/life11090911. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575060 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of internal cooling on physical performance, physiological and perceptional parameters when exercising in the heat: A systematic review with meta-analyses.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 11;14:1125969. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1125969. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37113693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eccles R. Menthol and related cooling compounds. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994;46:618–630. - PubMed
-
- Kamatou GPP, Vermaak I, Viljoen AM, Lawrence BM. Menthol: A simple monoterpene with remarkable biological properties. Phytochemistry. 2013;96:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Patel T, Ishiuji Y, Yosipovitch G. Menthol: A refreshing look at this ancient compound. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007;57:873–878. - PubMed
-
- Best R, Spears RI, Hurst P, Berger JAN. The development of a menthol solution for use during sport and exercise. Beverages. 2018;4:44.
-
- Stevens CJ, Best R. Menthol: A fresh ergogenic aid for athletic performance. Sports Med. 2017;47:1035–1042. - PubMed

