IQGAP1 causes choroidal neovascularization by sustaining VEGFR2-mediated Rac1 activation
- PMID: 32783108
- PMCID: PMC7530064
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-020-09740-y
IQGAP1 causes choroidal neovascularization by sustaining VEGFR2-mediated Rac1 activation
Abstract
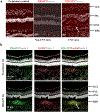
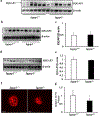
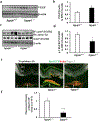
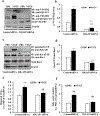
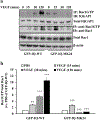
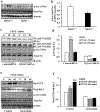
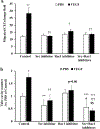
Loss of visual acuity in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) occurs when factors activate choroidal endothelial cells (CECs) to transmigrate the retinal pigment epithelium into the sensory retina and develop into choroidal neovascularization (CNV). Active Rac1 (Rac1GTP) is required for CEC migration and is induced by different AMD-related stresses, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Besides its role in pathologic events, Rac1 also plays a role in physiologic functions. Therefore, we were interested in a method to inhibit pathologic activation of Rac1. We addressed the hypothesis that IQGAP1, a scaffold protein with a Rac1 binding domain, regulates pathologic Rac1GTP in CEC migration and CNV. Compared to littermate Iqgap1+/+, Iqgap1-/- mice had reduced volumes of laser-induced CNV and decreased Rac1GTP and phosphorylated VEGFR2 (p-VEGFR2) within lectin-stained CNV. Knockdown of IQGAP1 in CECs significantly reduced VEGF-induced Rac1GTP, mediated through p-VEGFR2, which was necessary for CEC migration. Moreover, sustained activation of Rac1GTP induced by VEGF was eliminated when CECs were transfected with an IQGAP1 construct that is unable to bind Rac1. IQGAP1-mediated Src activation was involved in initiating Rac1 activation, CEC migration, and tube formation. Our findings indicate that CEC IQGAP1 interacts with VEGFR2 to mediate Src activation and subsequent Rac1 activation and CEC migration. In addition, IQGAP1 binding to Rac1GTP results in sustained activation of Rac1, leading to CEC migration toward VEGF. Our study supports a role of IQGAP1 and the interaction between IQGAP1 and Rac1GTP to restore CECs quiescence and, therefore, prevent vision-threatening CNV in nAMD.
Keywords: Age-related macular degeneration; IQGAP1; Rac1; Vascular endothelial growth factor; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; choroidal neovascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests
The authors declared there were no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Active Rap1-mediated inhibition of choroidal neovascularization requires interactions with IQGAP1 in choroidal endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2021 Jul;35(7):e21642. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100112R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34166557 Free PMC article.
-
Thy-1 Regulates VEGF-Mediated Choroidal Endothelial Cell Activation and Migration: Implications in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Oct 1;57(13):5525-5534. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19691. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27768790 Free PMC article.
-
The role of RPE cell-associated VEGF₁₈₉ in choroidal endothelial cell transmigration across the RPE.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Feb 1;52(1):570-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5595. Print 2011 Jan. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 20811045 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Rac1 Activation in Choroidal Endothelial Cells: Insights into Mechanisms in Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Cells. 2021 Sep 14;10(9):2414. doi: 10.3390/cells10092414. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of signaling events involved in the pathophysiology of neovascular AMD.Mol Vis. 2016 Feb 27;22:189-202. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27013848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active Rap1-mediated inhibition of choroidal neovascularization requires interactions with IQGAP1 in choroidal endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2021 Jul;35(7):e21642. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100112R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34166557 Free PMC article.
-
Chylomicrons Regulate Lacteal Permeability and Intestinal Lipid Absorption.Circ Res. 2023 Aug 4;133(4):333-349. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322607. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37462027 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting choroidal vascular dysfunction via inhibition of circRNA-FoxO1 for prevention and management of myopic pathology.Mol Ther. 2021 Jul 7;29(7):2268-2280. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.02.025. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33647458 Free PMC article.
-
Yap-Hippo Signaling Activates Mitochondrial Protection and Sustains Breast Cancer Viability under Hypoxic Stress.J Oncol. 2021 Sep 13;2021:5212721. doi: 10.1155/2021/5212721. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. Retraction in: J Oncol. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9814758. doi: 10.1155/2023/9814758 PMID: 34567116 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Pathological angiogenesis: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Angiogenesis. 2023 Aug;26(3):313-347. doi: 10.1007/s10456-023-09876-7. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Angiogenesis. 2023. PMID: 37060495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zarbin MA, Current concepts in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Archives of Ophthalmology, 2004. 122(4): p. 598–614. - PubMed
-
- Hartnett ME and Elsner AE, Characteristics of exudative age-related macular degeneration determined in vivo with confocal and indirect infrared imaging. Ophthalmology, 1996. 103(1): p. 58–71. - PubMed
-
- Freund KB, Zweifel SA, and Engelbert M, Do we need a new classification for choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration? Retina, 2010. 30(9): p. 1333–49. - PubMed
-
- Hartnett ME and Elsner AE, Characteristics of exudative age-related macular degeneration determined in vivo with confocal and indirect infrared imaging. Ophthalmology, 1996. 103: p. 58–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

