Biochanin-A ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-β mediated EMT, myofibroblasts differentiation and collagen deposition in in vitro and in vivo systems
- PMID: 32781391
- PMCID: PMC7395646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153298
Biochanin-A ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-β mediated EMT, myofibroblasts differentiation and collagen deposition in in vitro and in vivo systems
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive inflammatory disorder driven by a fibrotic cascade of events such as epithelial to mesenchymal transition, extracellular matrix production and collagen formation in the lungs in a sequential manner. IPF incidences were raising rapidly across the world. FDA approved pirfenidone and nintedanib (tyrosine kinase inhibitors) are being used as a first-line treatment drugs for IPF, however, neither the quality of life nor survival rates have been improved because of patient noncompliance due to multiple side effects. Thus, the development of novel therapeutic approaches targeting TGF-β mediated cascade of fibrotic events is urgently needed to improve the survival of the patients suffering from devastating disease.
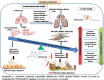
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate and validate the anti-fibrotic properties of Biochanin-A (isoflavone) against TGF-β mediated fibrosis in in vitro, ex vivo, in vivo models and to determine the molecular mechanisms that mediate these anti-fibrotic effects.
Methods: The therapeutic activity of BCA was determined in in vitro/ex vivo models. Cells were pre-treated with BCA and incubated in presence or absence of recombinant-TGF-β to stimulate the fibrotic cascade of events. Pulmonary fibrosis was developed by intratracheal administration of bleomycin in rats. BCA treatment was given for 14 days from post bleomycin instillation and then various investigations (collagen content, fibrosis gene/protein expression and histopathological changes) were performed to assess the anti-fibrotic activity of BCA.
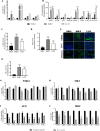
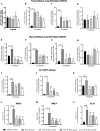
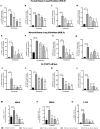
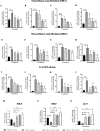
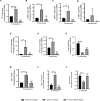
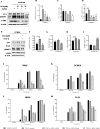
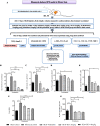
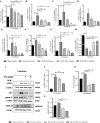
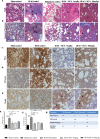
Results: In vitro/ex vivo (Primary normal, IPF cell line and primary IPF cells/ Precision cut mouse lung slices) experiments revealed that, BCA treatment significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the expression of TGF-β modulated fibrotic genes/protein expressions (including their functions) which are involved in the cascade of fibrotic events. BCA treatment significantly (p < 0.01) reduced the bleomycin-induced inflammatory cell-infiltration, inflammatory markers expression, collagen deposition and expression of fibrotic markers in lung tissues equivalent or better than pirfenidone treatment. In addition, BCA treatment significantly (p < 0.001) attenuated the TGF-β1/BLM-mediated increase of TGF-β/Smad2/3 phosphorylation and resulted in the reduction of pathological abnormalities in lung tissues determined by histopathology observations.
Conclusion: Collectively, BCA treatment demonstrated the remarkable therapeutic effects on TGF-β/BLM mediated pulmonary fibrosis using IPF cells and rodent models. This current study may offer a novel treatment approach to halt and may be even rescue the devastating lung scarring of IPF.
Keywords: BALF; Bleomycin; Collagen; Extra-cellular matrix; Inflammation; Myofibroblasts; TGF-β.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Andrographolide ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing cell proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation of fibroblasts via the TGF-β1-mediated Smad-dependent and -independent pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Mar 15;321:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31706003
-
Sulforaphane attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Apr 2;19(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0204-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29609658 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-β-dependent epithelial to mesenchymal transition.J Surg Res. 2015 Jul;197(1):167-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.02.062. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25911951
-
Use of the Reversible Myogenic to Lipogenic Transdifferentiation Switch for the Design of Pre-clinical Drug Screening in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Sep 15;8:569865. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.569865. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33042971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation induces the differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblasts via the miR-21/PTEN pathway.Respir Res. 2023 Nov 28;24(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02606-z. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 38017523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biochanin A Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in Mice by Modulating the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways.Inflammation. 2024 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02103-5. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39017810
-
Sinigrin Attenuates the Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating the MAPK Pathway.Inflammation. 2023 Jun;46(3):787-807. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01780-4. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36622573
-
Naringin regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitophagy through the ATF3/PINK1 signaling axis to alleviate pulmonary fibrosis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;396(6):1155-1169. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02390-z. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36688958
-
Identification of Hub Genes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Their Association with Lung Cancer by Bioinformatics Analysis.Adv Respir Med. 2023 Oct 12;91(5):407-431. doi: 10.3390/arm91050032. Adv Respir Med. 2023. PMID: 37887075 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable photocurable Janus hydrogel delivering hiPSC cardiomyocyte-derived exosome for post-heart surgery adhesion reduction.Sci Adv. 2023 Aug 4;9(31):eadh1753. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh1753. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37540739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akgedik R., Akgedik Ş., Karamanlı H., Uysal S., Bozkurt B., Ozol D., Armutcu F., Yıldırım Z. Effect of Resveratrol on Treatment of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats. Inflammation. 2012;35:1732–1741. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

