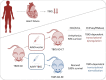
Preclinical evidence for the therapeutic value of TBX5 normalization in arrhythmia control
- PMID: 32777030
- PMCID: PMC8262635
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa239
Preclinical evidence for the therapeutic value of TBX5 normalization in arrhythmia control
Abstract
Aims: Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death (SCD) occur commonly in patients with heart failure. We found T-box 5 (TBX5) dysregulated in ventricular myocardium from heart failure patients and thus we hypothesized that TBX5 reduction contributes to arrhythmia development in these patients. To understand the underlying mechanisms, we aimed to reveal the ventricular TBX5-dependent transcriptional network and further test the therapeutic potential of TBX5 level normalization in mice with documented arrhythmias.
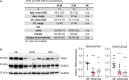
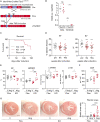
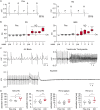
Methods and results: We used a mouse model of TBX5 conditional deletion in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Ventricular (v) TBX5 loss in mice resulted in mild cardiac dysfunction and arrhythmias and was associated with a high mortality rate (60%) due to SCD. Upon angiotensin stimulation, vTbx5KO mice showed exacerbated cardiac remodelling and dysfunction suggesting a cardioprotective role of TBX5. RNA-sequencing of a ventricular-specific TBX5KO mouse and TBX5 chromatin immunoprecipitation was used to dissect TBX5 transcriptional network in cardiac ventricular tissue. Overall, we identified 47 transcripts expressed under the control of TBX5, which may have contributed to the fatal arrhythmias in vTbx5KO mice. These included transcripts encoding for proteins implicated in cardiac conduction and contraction (Gja1, Kcnj5, Kcng2, Cacna1g, Chrm2), in cytoskeleton organization (Fstl4, Pdlim4, Emilin2, Cmya5), and cardiac protection upon stress (Fhl2, Gpr22, Fgf16). Interestingly, after TBX5 loss and arrhythmia development in vTbx5KO mice, TBX5 protein-level normalization by systemic adeno-associated-virus (AAV) 9 application, re-established TBX5-dependent transcriptome. Consequently, cardiac dysfunction was ameliorated and the propensity of arrhythmia occurrence was reduced.
Conclusions: This study uncovers a novel cardioprotective role of TBX5 in the adult heart and provides preclinical evidence for the therapeutic value of TBX5 protein normalization in the control of arrhythmia.
Keywords: AAV9 in vivo re-expression; Arrhythmia; Heart failure; T-box 5; Sudden cardiac death.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional Patterning of the Ventricular Cardiac Conduction System.Circ Res. 2020 Jul 17;127(3):e94-e106. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314460. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32290757 Free PMC article.
-
A gene therapeutic approach to inhibit calcium and integrin binding protein 1 ameliorates maladaptive remodelling in pressure overload.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Jan 1;115(1):71-82. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy154. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 29931050
-
TBX5 drives Scn5a expression to regulate cardiac conduction system function.J Clin Invest. 2012 Jul;122(7):2509-18. doi: 10.1172/JCI62617. Epub 2012 Jun 25. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22728936 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden Cardiac Death Substrate Imaged by Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Investigational Tool to Clinical Applications.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017 Jul;10(7):e005461. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.005461. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28637807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased left ventricular mass as a predictor of sudden cardiac death: is it time to put it to the test?Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013 Feb;6(1):212-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.112.974931. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23424223 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the secrets of Cardiac development and function: the critical role of FHL2.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Oct 28. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05142-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39466483 Review.
-
Swimming exercise with L-arginine coated nanoparticles supplementation upregulated HAND2 and TBX5 expression in the cardiomyocytes of aging male rats.Biogerontology. 2022 Aug;23(4):473-484. doi: 10.1007/s10522-022-09977-8. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Biogerontology. 2022. PMID: 35809117
-
Cardiomyopathies in Children and Systemic Disorders When Is It Useful to Look beyond the Heart?J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Jan 31;9(2):47. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9020047. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 35200700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Transcription Factor Tbx5-Dependent Epigenetic Modification Contributes to Neuropathic Allodynia by Activating TRPV1 Expression in the Dorsal Horn.J Neurosci. 2024 Sep 25;44(39):e0497242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0497-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39174351
-
Transcriptome and open chromatin analysis reveals the process of myocardial cell development and key pathogenic target proteins in Long QT syndrome type 7.J Transl Med. 2024 Mar 25;22(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05125-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38528561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horb ME, Thomsen GH.. Tbx5 is essential for heart development. Development 1999;126:1739–1751. - PubMed
-
- Basson CT, Bachinsky DR, Lin RC, Levi T, Elkins JA, Soults J, Grayzel D, Kroumpouzou E, Traill TA, Leblanc-Straceski J, Renault B, Kucherlapati R, Seidman JG, Seidman CE.. Mutations in human TBX5 [corrected] cause limb and cardiac malformation in Holt-Oram syndrome. Nat Genet 1997;15:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Holm H, Gudbjartsson DF, Arnar DO, Thorleifsson G, Thorgeirsson G, Stefansdottir H, Gudjonsson SA, Jonasdottir A, Mathiesen EB, Njolstad I, Nyrnes A, Wilsgaard T, Hald EM, Hveem K, Stoltenberg C, Lochen ML, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K.. Several common variants modulate heart rate, PR interval and QRS duration. Nat Genet 2010;42:117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

