Establishing Simultaneous T Cell Receptor Excision Circles (TREC) and K-Deleting Recombination Excision Circles (KREC) Quantification Assays and Laboratory Reference Intervals in Healthy Individuals of Different Age Groups in Hong Kong
- PMID: 32765500
- PMCID: PMC7378446
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01411
Establishing Simultaneous T Cell Receptor Excision Circles (TREC) and K-Deleting Recombination Excision Circles (KREC) Quantification Assays and Laboratory Reference Intervals in Healthy Individuals of Different Age Groups in Hong Kong
Abstract
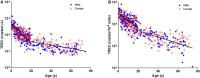
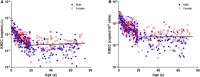
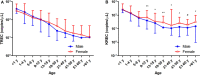
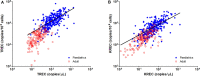
The clinical experience gathered throughout the years has raised awareness of primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDD). T cell receptor excision circles (TREC) and kappa-deleting recombination excision circles (KREC) assays for thymic and bone marrow outputs measurement have been widely implemented in newborn screening (NBS) programs for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. The potential applications of combined TREC and KREC assay in PIDD diagnosis and immune reconstitution monitoring in non-neonatal patients have been suggested. Given that ethnicity, gender, and age can contribute to variations in immunity, defining the reference intervals of TREC and KREC levels in the local population is crucial for setting up cut-offs for PIDD diagnosis. In this retrospective study, 479 healthy Chinese sibling donors (240 males and 239 females; age range: 1 month-74 years) from Hong Kong were tested for TREC and KREC levels using a simultaneous quantitative real-time PCR assay. Age-specific 5th-95th percentile reference intervals of TREC and KREC levels (expressed in copies per μL blood and copies per 106 cells) were established in both pediatric and adult age groups. Significant inverse correlations between age and both TREC and KREC levels were observed in the pediatric age group. A significant higher KREC level was observed in females than males after 9-12 years of age but not for TREC. Low TREC or KREC levels were detected in patients diagnosed with mild or severe PIDD. This assay with the established local reference intervals would allow accurate diagnosis of PIDD, and potentially monitoring immune reconstitution following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation or highly active anti-retroviral therapy in the future.
Keywords: K-deleting recombination excision circles; T cell receptor excision circles; immune reconstitution; primary immunodeficiency; reference interval.
Copyright © 2020 Kwok, Cheung, Ho, Tang, Chu, Leung, Lee, Cheuk, Lee, Ip and Lau.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Multiplex, Droplet Digital PCR Assay for the Detection of T-Cell Receptor Excision Circles and Kappa-Deleting Recombination Excision Circles.Clin Chem. 2020 Jan 1;66(1):229-238. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2019.308171. Clin Chem. 2020. PMID: 31672859
-
Determining Laboratory Reference Values of TREC and KREC in Different Age Groups of Iranian Healthy Individuals.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019 Apr 1;18(2):143-152. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31066250
-
The TREC/KREC assay for the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with DiGeorge syndrome.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 8;9(12):e114514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114514. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25485546 Free PMC article.
-
Newborn Screening through TREC, TREC/KREC System for Primary Immunodeficiency with limitation of TREC/KREC. Comprehensive Review.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2021;20(2):132-149. doi: 10.2174/1871523019999200730171600. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32748762 Review.
-
Use of V(D)J recombination excision circles to identify T- and B-cell defects and to monitor the treatment in primary and acquired immunodeficiencies.J Transl Med. 2013 May 9;11:119. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-119. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23656963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune aging: biological mechanisms, clinical symptoms, and management in lung transplant recipients.Front Transplant. 2024 Feb 8;3:1356948. doi: 10.3389/frtra.2024.1356948. eCollection 2024. Front Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38993782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of TREC and KREC as molecular markers for immunological evaluation of down syndrome children.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 18;13(1):15445. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42370-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37723211 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel CDC42 Variant with Impaired Thymopoiesis, IL-7R Signaling, PAK1 Binding, and TCR Repertoire Diversity.J Clin Immunol. 2023 Nov;43(8):1927-1940. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01561-0. Epub 2023 Aug 15. J Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37581646 Free PMC article.
-
Two patients with ZAP-70 deficiency in China present with a different genetic, immunological, and clinical phenotype.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Apr 26;23(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-03975-6. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37101133 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring T-Cell Kinetics in the Early Recovery Period of Lung Transplantation Cases by Copy Number Levels of T-Cell Receptor Excision Circle.In Vivo. 2023 Jan-Feb;37(1):310-319. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13081. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 36593057 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

