Spinal Inhibition of GABAB Receptors by the Extracellular Matrix Protein Fibulin-2 in Neuropathic Rats
- PMID: 32765223
- PMCID: PMC7378325
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00214
Spinal Inhibition of GABAB Receptors by the Extracellular Matrix Protein Fibulin-2 in Neuropathic Rats
Abstract
In the central nervous system, the inhibitory GABAB receptor is the archetype of heterodimeric G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Receptor interaction with partner proteins has emerged as a novel mechanism to alter GPCR signaling in pathophysiological conditions. We propose here that GABAB activity is inhibited through the specific binding of fibulin-2, an extracellular matrix protein, to the B1a subunit in a rat model of neuropathic pain. We demonstrate that fibulin-2 hampers GABAB activation, presumably through decreasing agonist-induced conformational changes. Fibulin-2 regulates the GABAB-mediated presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmitter release and weakens the GABAB-mediated inhibitory effect in neuronal cell culture. In the dorsal spinal cord of neuropathic rats, fibulin-2 is overexpressed and colocalized with B1a. Fibulin-2 may thus interact with presynaptic GABAB receptors, including those on nociceptive afferents. By applying anti-fibulin-2 siRNA in vivo, we enhanced the antinociceptive effect of intrathecal baclofen in neuropathic rats, thus demonstrating that fibulin-2 limits the action of GABAB agonists in vivo. Taken together, our data provide an example of an endogenous regulation of GABAB receptor by extracellular matrix proteins and demonstrate its functional impact on pathophysiological processes of pain sensitization.
Keywords: GABAB receptor; disinhibition; fibulin-2; neuropathic pain; spinal cord.
Copyright © 2020 Papon, Le Feuvre, Barreda-Gómez, Favereaux, Farrugia, Bouali-Benazzouz, Nagy, Rodríguez-Puertas and Landry.
Figures
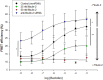
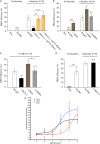
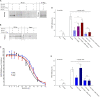
 ); anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (
); anti-fibulin-2 siRNA ( ) controls (■). pIC50control: –5.0 ± 0.1; pIC50siRNA: –4.6 ± 0.1; pIC50fibulin: –4.7 ± 0.1. (D) Effects of saclofen on FRET efficiency between GFP-GABAB1a and DsRed-GABAB2 ± baclofen at 10–6M. Baclofen effect is reversed by saclofen at 100 μM and 1 mM. Application of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (20 or 40 pmol) suppresses this reversion at 100 μM dose (***p < 0.001 “B1a/B2 + saclo100 μM” vs. “B1a/B2 + saclo100 μM + siRNA40”). At high dose (1 mM), saclofen remains efficient even in the presence of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (NS: p > 0.05 “B1a/B2 + saclo1 mM” vs. “B1a/B2 + saclo1 mM + siRNA40”) (n = 21 cells). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s.: p > 0.05 vs. “B1a/B2 + baclofen” unless indicated. (E) Effects of CGP55845 on FRET efficiency between GFP-GABAB1a and DsRed-GABAB2 ± baclofen at 10–6M. Baclofen effect is reversed by CGP55845 at 0.5 and 50 μM. Application of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (40 pmol) suppresses this reversion at 0.5 μM dose (*p < 0.05 “B1a/B2 + CGP 0.5 μM” vs. “B1a/B2 + CGP 0.5 μM + siRNA40”). At high dose (50 μM), CGP remains efficient even in the presence of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (NS: p > 0.05 “B1a/B2 + CGP50 μM” vs. “B1a/B2 + CGP50 μM + siRNA40”) (n = 21 cells). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s.: p > 0.05 vs. “B1a/B2 + baclofen” unless indicated.
) controls (■). pIC50control: –5.0 ± 0.1; pIC50siRNA: –4.6 ± 0.1; pIC50fibulin: –4.7 ± 0.1. (D) Effects of saclofen on FRET efficiency between GFP-GABAB1a and DsRed-GABAB2 ± baclofen at 10–6M. Baclofen effect is reversed by saclofen at 100 μM and 1 mM. Application of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (20 or 40 pmol) suppresses this reversion at 100 μM dose (***p < 0.001 “B1a/B2 + saclo100 μM” vs. “B1a/B2 + saclo100 μM + siRNA40”). At high dose (1 mM), saclofen remains efficient even in the presence of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (NS: p > 0.05 “B1a/B2 + saclo1 mM” vs. “B1a/B2 + saclo1 mM + siRNA40”) (n = 21 cells). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s.: p > 0.05 vs. “B1a/B2 + baclofen” unless indicated. (E) Effects of CGP55845 on FRET efficiency between GFP-GABAB1a and DsRed-GABAB2 ± baclofen at 10–6M. Baclofen effect is reversed by CGP55845 at 0.5 and 50 μM. Application of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (40 pmol) suppresses this reversion at 0.5 μM dose (*p < 0.05 “B1a/B2 + CGP 0.5 μM” vs. “B1a/B2 + CGP 0.5 μM + siRNA40”). At high dose (50 μM), CGP remains efficient even in the presence of anti-fibulin-2 siRNA (NS: p > 0.05 “B1a/B2 + CGP50 μM” vs. “B1a/B2 + CGP50 μM + siRNA40”) (n = 21 cells). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s.: p > 0.05 vs. “B1a/B2 + baclofen” unless indicated.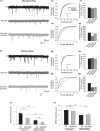
Similar articles
-
Impairment of GABAB receptor dimer by endogenous 14-3-3ζ in chronic pain conditions.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 1;31(15):3239-51. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.161. Epub 2012 Jun 12. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22692127 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of spinal GABAB receptors normalizes N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in diabetic neuropathy.J Neurol Sci. 2014 Jun 15;341(1-2):68-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 12. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24787504
-
The positive allosteric GABAB receptor modulator rac-BHFF enhances baclofen-mediated analgesia in neuropathic mice.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Sep;108:172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.04.028. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27108932
-
Clinical potential of GABAB receptor modulators.CNS Drug Rev. 2005 Autumn;11(3):317-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2005.tb00049.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2005. PMID: 16389296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of GABA in the mediation and perception of pain.Adv Pharmacol. 2006;54:1-27. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(06)54001-3. Adv Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17175808 Review.
Cited by
-
The cell adhesion molecule CD44 acts as a modulator of 5-HT7 receptor functions.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Nov 23;22(1):563. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01931-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39580460 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Inhibition of Pain and Touch in the Spinal Cord: From Receptors to Circuits.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 2;22(1):414. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010414. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33401784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell transcriptomic profile of satellite glial cells in trigeminal ganglion.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Feb 2;16:1117065. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1117065. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36818656 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

