The OXA2a Insertase of Arabidopsis Is Required for Cytochrome c Maturation
- PMID: 32759271
- PMCID: PMC7536658
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.19.01248
The OXA2a Insertase of Arabidopsis Is Required for Cytochrome c Maturation
Abstract
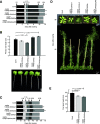
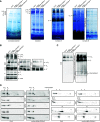
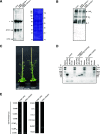
In yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and human (Homo sapiens) mitochondria, Oxidase assembly protein1 (Oxa1) is the general insertase for protein insertion from the matrix side into the inner membrane while Cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein18 (Cox18/Oxa2) is specifically involved in the topogenesis of the complex IV subunit, Cox2. Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) mitochondria contain four OXA homologs: OXA1a, OXA1b, OXA2a, and OXA2b. OXA2a and OXA2b are unique members of the Oxa1 superfamily, in that they possess a tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain at their C termini. Here, we determined the role of OXA2a by studying viable mutant plants generated by partial complementation of homozygous lethal OXA2a transfer-DNA insertional mutants using the developmentally regulated ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE3 (ABI3) promoter. The ABI3p:OXA2a plants displayed growth retardation due to a reduction in the steady-state abundances of both c-type cytochromes, cytochrome c 1 and cytochrome c The observed reduction in the steady-state abundance of complex III could be attributed to cytochrome c 1 being one of its subunits. Expression of a soluble heme lyase from an organism with cytochrome c maturation system III could functionally complement the lack of OXA2a. This implies that OXA2a is required for the system I cytochrome c maturation of Arabidopsis. Due to the interaction of OXA2a with Cytochrome c maturation protein CcmF C-terminal-like protein (CCMFC) in a yeast split-ubiquitin based interaction assay, we propose that OXA2a aids in the membrane insertion of CCMFC, which is presumed to form the heme lyase component of the cytochrome c maturation pathway. In contrast with the crucial role played by the TPR domain of OXA2b, the TPR domain of OXA2a is not essential for its functionality.
© 2020 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
OXA2b is Crucial for Proper Membrane Insertion of COX2 during Biogenesis of Complex IV in Plant Mitochondria.Plant Physiol. 2019 Feb;179(2):601-615. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01286. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30487140 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana Oxa proteins locate to mitochondria and fulfill essential roles during embryo development.Planta. 2013 Feb;237(2):573-88. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1793-9. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23179441
-
A novel pathway of cytochrome c biogenesis is involved in the assembly of the cytochrome b6f complex in arabidopsis chloroplasts.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 5;283(36):24608-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803869200. Epub 2008 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18593701 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Oxa1-related inner-membrane translocases in assembly of respiratory chain complexes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1793(1):60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.05.004. Epub 2008 May 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18522806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox processes controlling the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010 Nov 1;13(9):1385-401. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3161. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010. PMID: 20214494 Review.
Cited by
-
The biogenesis and regulation of the plant oxidative phosphorylation system.Plant Physiol. 2023 May 31;192(2):728-747. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad108. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36806687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen JW, Jackson AP, Rigden DJ, Willis AC, Ferguson SJ, Ginger ML(2008) Order within a mosaic distribution of mitochondrial c-type cytochrome biogenesis systems? FEBS J 275: 2385–2402 - PubMed
-
- Asseck LY, Grefen C(2018) Detecting interactions of membrane proteins: The split-ubiquitin system. Methods Mol Biol 1794: 49–60 - PubMed
-
- Baerenfaller K, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Svozil J, Hull R, Russenberger D, Bischof S, Lu Q, Gruissem W, Baginsky S(2011) pep2pro: A new tool for comprehensive proteome data analysis to reveal information about organ-specific proteomes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Integr Biol 3: 225–237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

