Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian fibroblast growth factor genes
- PMID: 32758140
- PMCID: PMC7430813
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-020-06958-4
Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian fibroblast growth factor genes
Abstract
Background: The eutherian fibroblast growth factors were implicated as key regulators in developmental processes. However, there were major disagreements in descriptions of comprehensive eutherian fibroblast growth factors gene data sets including either 18 or 22 homologues. The present analysis attempted to revise and update comprehensive eutherian fibroblast growth factor gene data sets, and address and resolve major discrepancies in their descriptions using eutherian comparative genomic analysis protocol and 35 public eutherian reference genomic sequence data sets.
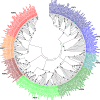
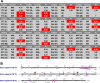
Results: Among 577 potential coding sequences, the tests of reliability of eutherian public genomic sequences annotated most comprehensive curated eutherian third-party data gene data set of fibroblast growth factor genes including 267 complete coding sequences. The present study first described 8 superclusters including 22 eutherian fibroblast growth factor major gene clusters, proposing their updated classification and nomenclature.
Conclusions: The integrated gene annotations, phylogenetic analysis and protein molecular evolution analysis argued that comprehensive eutherian fibroblast growth factor gene data set classifications included 22 rather than 18 homologues.
Keywords: Eutheria; Gene annotations; Molecular evolution; Phylogenetic analysis; RRID:SCR_014401.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian interferon genes.Genomics. 2020 Nov;112(6):4749-4759. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.08.029. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32871222
-
Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian connexin genes.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 15;9(1):16938. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53458-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31729432 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian kallikrein genes.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2017 Feb 3;10:96-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2017.01.009. eCollection 2017 Mar. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2017. PMID: 28224083 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian interferon-γ-inducible GTPases.Funct Integr Genomics. 2012 Nov;12(4):599-607. doi: 10.1007/s10142-012-0291-2. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Funct Integr Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22892676 Review.
-
Molecular evolution of the neurohypophysial hormone precursors in mammals: Comparative genomics reveals novel mammalian oxytocin and vasopressin analogues.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2012 Nov 1;179(2):313-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.07.030. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22995712 Review.
Cited by
-
Revised eutherian gene collections.BMC Genom Data. 2022 Jul 23;23(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12863-022-01071-9. BMC Genom Data. 2022. PMID: 35870891 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

