Erythropoietin receptor in B cells plays a role in bone remodeling in mice
- PMID: 32754275
- PMCID: PMC7392011
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.45845
Erythropoietin receptor in B cells plays a role in bone remodeling in mice
Abstract
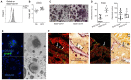
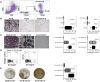
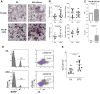
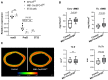
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a key regulator of erythropoiesis. However, EPO receptors (EPO-Rs) are also expressed on non-erythroid cell types, including myeloid and bone cells. Immune cells also participate in bone homeostasis. B cells produce receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG), two pivotal regulators of bone metabolism. Here we explored the ability of B cells to transdifferentiate into functional osteoclasts and examined the role of EPO in this process in a murine model. Methods: We have combined specifically-designed experimental mouse models and in vitro based osteoclastogenesis assays, as well as PCR analysis of gene expression. Results: (i) EPO treatment in vivo increased RANKL expression in bone marrow (BM) B cells, suggesting a paracrine effect on osteoclastogenesis; (ii) B cell-derived osteoclastogenesis occured in vivo and in vitro, as demonstrated by B cell lineage tracing in murine models; (iii) B-cell-derived osteoclastogenesis in vitro was restricted to Pro-B cells expressing CD115/CSF1-R and is enhanced by EPO; (iv) EPO treatment increased the number of B-cell-derived preosteoclasts (β3+CD115+), suggesting a physiological rationale for B cell derived osteoclastogenesis; (v) finally, mice with conditional EPO-R knockdown in the B cell lineage (cKD) displayed a higher cortical and trabecular bone mass. Moreover, cKD displayed attenuated EPO-driven trabecular bone loss, an effect that was observed despite the fact that cKD mice attained higher hemoglobin levels following EPO treatment. Conclusions: Our work highlights B cells as an important extra-erythropoietic target of EPO-EPO-R signaling and suggests their involvement in the regulation of bone homeostasis and possibly in EPO-stimulated erythropoietic response. Importantly, we present here for the first time, histological evidence for B cell-derived osteoclastogenesis in vivo.
Keywords: Pro-B cells; bone marrow; cFMS/CD115/CSF1R; erythropoietin; lymphocytes; osteoclastogenesis; transdifferentiation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erythropoietin Receptor (EPOR) Signaling in the Osteoclast Lineage Contributes to EPO-Induced Bone Loss in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12051. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912051. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233351 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin couples erythropoiesis, B-lymphopoiesis, and bone homeostasis within the bone marrow microenvironment.Blood. 2011 May 26;117(21):5631-42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-320564. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21421837
-
Erythropoietin directly stimulates osteoclast precursors and induces bone loss.FASEB J. 2015 May;29(5):1890-900. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-259085. Epub 2015 Jan 28. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25630969
-
Erythropoietin (EPO) as a Key Regulator of Erythropoiesis, Bone Remodeling and Endothelial Transdifferentiation of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): Implications in Regenerative Medicine.Cells. 2021 Aug 20;10(8):2140. doi: 10.3390/cells10082140. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Jan;39(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01162-6. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33079279 Review.
Cited by
-
Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel loading erythropoietin and FK506 alleviates gingival inflammation and promotes periodontal tissue regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 4;11:1323554. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1323554. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38239915 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin Non-hematopoietic Tissue Response and Regulation of Metabolism During Diet Induced Obesity.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 15;12:725734. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.725734. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34603036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin Receptor (EPOR) Signaling in the Osteoclast Lineage Contributes to EPO-Induced Bone Loss in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12051. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912051. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233351 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Signaling in Osteogenesis and Skeletal Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 23;23(19):11201. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911201. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin: A Personal Alice in Wonderland Trip in the Shadow of the Giants.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 27;14(4):408. doi: 10.3390/biom14040408. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin after a century of research: younger than ever. Eur J Haematol. 2007;78:183–205. - PubMed
-
- Park S, Greenberg P, Yucel A, Farmer C, O'Neill F, De Oliveira Brandao C. et al. Clinical effectiveness and safety of erythropoietin-stimulating agents for the treatment of low- and intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: a systematic literature review. Br J Haematol. 2019;184:134–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

