The Expression and Therapeutic Potential of Checkpoint Kinase 2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 32753843
- PMCID: PMC7351626
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S245267
The Expression and Therapeutic Potential of Checkpoint Kinase 2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) is the most common histological subtype of laryngeal cancer. The involved molecular mechanisms and suitable therapeutic targets for LSCC still need to be further investigated. Checkpoint kinase 2 (CHK2) participates in several cellular physiology pathways and plays a role in tumor progression. However, the roles of CHK2 in LSCC remain unclear.
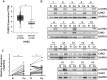
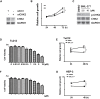
Methods: mRNA expression data were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, and bioinformatic analysis was performed. Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses were conducted to detect protein expression. MTS assays were performed to examine cell growth of LSCC-derived cell lines.
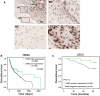
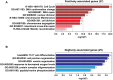
Results: In the present study, we found that both active form of CHK2 and total CHK2 protein expressions were up-regulated in LSCC tissues. Positive expression of CHK2 was closely associated with advanced clinical features and poor prognosis. Moreover, potential CHK2-involving bioprocesses and signaling pathways were analyzed. In addition, repressed proliferation of LSCC cells was induced by CHK2 inhibitor.
Discussion: Taken together, our findings elucidated that CHK2 may act as an oncogenic factor in LSCC, suggesting a potential target for clinical treatment.
Keywords: BML-277; checkpoint kinase 2; laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma; tumor growth.
© 2020 Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
circPARD3 drives malignant progression and chemoresistance of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting autophagy through the PRKCI-Akt-mTOR pathway.Mol Cancer. 2020 Nov 24;19(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01279-2. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33234130 Free PMC article.
-
HOX genes: potential candidates for the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):15087-15096. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5356-8. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27658780
-
Zinc finger protein x-linked (ZFX) contributes to patient prognosis, cell proliferation and apoptosis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 1;8(11):13886-99. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26823701 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑195 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting ROCK1.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):7154-7162. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7460. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28901478
-
[Relationship between SLP-2 expression and prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and mammary invasive carcinoma].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010 May;39(5):332-7. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20654157 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Could Inhibiting the DNA Damage Repair Checkpoint Rescue Immune-Checkpoint-Inhibitor-Resistant Endometrial Cancer?J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 20;12(8):3014. doi: 10.3390/jcm12083014. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

