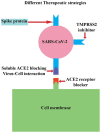
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and SARS-CoV-2: Potential therapeutic targeting
- PMID: 32745604
- PMCID: PMC7834210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173455
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and SARS-CoV-2: Potential therapeutic targeting
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a beta coronavirus that uses the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor as a point of entry. The present review discusses the origin and structure of the virus and its mechanism of cell entry followed by the therapeutic potentials of strategies directed towards SARS-CoV2-ACE2 binding, the renin-angiotensin system, and the kinin-kallikrein system. SARS-CoV2-ACE2 binding-directed approaches mainly consist of targeting receptor binding domain, ACE2 blockers, soluble ACE2, and host protease inhibitors. In conclusion, blocking or manipulating the SARS-CoV2-ACE2 binding interface perhaps offers the best tactic against the virus that should be treated as a fundamental subject of future research.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; Origin; SARS-CoV2; Therapeutic; Transmission.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jun 12;10(16):7448-7464. doi: 10.7150/thno.48076. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32642005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could a specific ACE2 activator drug improve the clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2? A potential pharmacological insight.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;13(8):807-811. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2020.1798760. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32686527 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Coevolution, Dynamics and Allostery Conspire in Shaping Cooperative Binding and Signal Transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein with Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 4;21(21):8268. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218268. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33158276 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Inhibitors by Drug Repurposing Using in silico Structure-Based Virtual Screening Approach.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 10;11:1664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01664. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32754161 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanistic overview of SARS-CoV-2 using angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 to enter the cell for replication: possible treatment options related to the renin-angiotensin system.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020 Sep 1;6(5):317-325. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa053. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32464637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Introduction on Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic: The Global Challenge.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1318:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-63761-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33973169
-
Prevalence, risk factors and characterisation of individuals with long COVID using Electronic Health Records in over 1.5 million COVID cases in England.J Infect. 2024 Oct;89(4):106235. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106235. Epub 2024 Aug 7. J Infect. 2024. PMID: 39121972 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-specific plant and microbial lectins as antiviral agents: A review.Glycoconj J. 2024 Feb;41(1):1-33. doi: 10.1007/s10719-023-10142-7. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Glycoconj J. 2024. PMID: 38244136 Review.
-
The Impact of the SARS-COV-2 Pandemic on the Mental Health and Employment Decisions of Medical Students in North China.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 19;12:641138. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.641138. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34349677 Free PMC article.
-
Computational drug discovery and repurposing for the treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Jan;106:104490. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104490. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33261845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abelous J. Les substances hypotensives de l'urine humaine normale. CR Soc Biol. 1909;66:511–512.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous