Optimization of Culture Conditions for Maintaining Pig Muscle Stem Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 32734272
- PMCID: PMC7372987
- DOI: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e39
Optimization of Culture Conditions for Maintaining Pig Muscle Stem Cells In Vitro
Abstract
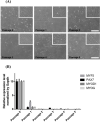
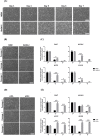
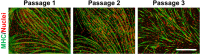
Muscle stem cells isolated from domestic animals, including cows and pigs, were recently spotlighted as candidates for the production of alternative protein resources, so-called cultured meat or lab-grown meat. In the present study, we aimed to optimize the in vitro culture conditions for the long-term expansion of pig muscle stem cells via the screening of various signaling molecules. Pig muscle stem cells were collected from the biceps femoris muscles of 3-d-old crossbred pigs (Landrace×Yorkshire×Duroc, LYD) and cultured in minimum essential medium-based growth media. However, the pig muscle stem cells gradually lost their proliferation ability and featured morphologies during the long-term culture over two weeks. To find suitable in vitro culture conditions for an extended period, skeletal muscle growth medium-2, including epidermal growth factor (EGF), dexamethasone, and a p38 inhibitor (SB203580), was used to support the stemness of the pig muscle stem cells. Interestingly, pig muscle stem cells were stably maintained in a long-term culture without loss of the expression of myogenic marker genes as determined by PCR analysis. Immunostaining analysis showed that the stem cells were capable of myogenic differentiation after multiple passaging. Therefore, we found that basal culture conditions containing EGF, dexamethasone, and a p38 inhibitor were suitable for maintaining pig muscle stem cells during expanded culture in vitro. This culture method may be applied for the production of cultured meat and further basic research on muscle development in the pig.
Keywords: EGF; dexamethasone; muscle stem cells; p38 inhibitor; pig.
© Korean Society for Food Science of Animal Resources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Purification of Pig Muscle Stem Cells Using Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS) Based on the Expression of Cluster of Differentiation 29 (CD29).Food Sci Anim Resour. 2020 Sep;40(5):852-859. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e51. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2020. PMID: 32968735 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic changes in culture media with varying passage numbers of pig muscle stem cell culture for cultured meat production.Food Res Int. 2024 Apr;182:114138. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114138. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38519170
-
Growth factors improve the proliferation of Jeju black pig muscle cells by regulating myogenic differentiation 1 and growth-related genes.Anim Biosci. 2021 Aug;34(8):1392-1402. doi: 10.5713/ab.20.0585. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33561926 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle stem cell isolation and in vitro culture for meat production: A methodological review.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021 Jan;20(1):429-457. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12661. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021. PMID: 33443788 Review.
-
Cultured meat from stem cells: challenges and prospects.Meat Sci. 2012 Nov;92(3):297-301. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Meat Sci. 2012. PMID: 22543115 Review.
Cited by
-
A scoping review of cultivated meat techno-economic analyses to inform future research directions for scaled-up manufacturing.Nat Food. 2024 Nov;5(11):901-910. doi: 10.1038/s43016-024-01061-3. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Nat Food. 2024. PMID: 39424999
-
Biological activity and processing technologies of edible insects: a review.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 5;30(8):1003-1023. doi: 10.1007/s10068-021-00942-8. eCollection 2021 Aug. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34471556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review: 3D bioprinting of cultured muscle meat and seafood products and its potential for the food industry.Trends Food Sci Technol. 2024 Oct;152:104670. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104670. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39309029
-
Combination of cell signaling molecules can facilitate MYOD1-mediated myogenic transdifferentiation of pig fibroblasts.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021 May 13;12(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00583-1. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33980301 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of Pig Muscle Stem Cells Using Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS) Based on the Expression of Cluster of Differentiation 29 (CD29).Food Sci Anim Resour. 2020 Sep;40(5):852-859. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2020.e51. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2020. PMID: 32968735 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

