Population variation in miRNAs and isomiRs and their impact on human immunity to infection
- PMID: 32731901
- PMCID: PMC7391576
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02098-w
Population variation in miRNAs and isomiRs and their impact on human immunity to infection
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators of the immune system, yet their variation and contribution to intra- and inter-population differences in immune responses is poorly characterized.
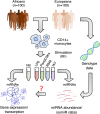
Results: We generate 977 miRNA-sequencing profiles from primary monocytes from individuals of African and European ancestry following activation of three TLR pathways (TLR4, TLR1/2, and TLR7/8) or infection with influenza A virus. We find that immune activation leads to important modifications in the miRNA and isomiR repertoire, particularly in response to viral challenges. These changes are much weaker than those observed for protein-coding genes, suggesting stronger selective constraints on the miRNA response to stimulation. This is supported by the limited genetic control of miRNA expression variability (miR-QTLs) and the lower occurrence of gene-environment interactions, in stark contrast with eQTLs that are largely context-dependent. We also detect marked differences in miRNA expression between populations, which are mostly driven by non-genetic factors. On average, miR-QTLs explain approximately 60% of population differences in expression of their cognate miRNAs and, in some cases, evolve adaptively, as shown in Europeans for a miRNA-rich cluster on chromosome 14. Finally, integrating miRNA and mRNA data from the same individuals, we provide evidence that the canonical model of miRNA-driven transcript degradation has a minor impact on miRNA-mRNA correlations, which are, in our setting, mainly driven by co-transcription.
Conclusion: Together, our results shed new light onto the factors driving miRNA and isomiR diversity at the population level and constitute a useful resource for evaluating their role in host differences of immunity to infection.
Keywords: Immunity; Isoforms; Population; miR-QTLs; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A highly expressed miR-101 isomiR is a functional silencing small RNA.BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 15;14:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-104. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23414127 Free PMC article.
-
IsomiR-eQTL: A Cancer-Specific Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Database of miRNAs and Their Isoforms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12493. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012493. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293349 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the one-locus-one-miRNA paradigm: microRNA isoforms enable deeper insights into breast cancer heterogeneity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 30;43(19):9158-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv922. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26400174 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
IsomiRs: Expanding the miRNA repression toolbox beyond the seed.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Apr;1863(4):194373. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 30953728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-4482 and miR-3912 aim for 3'UTR of ERG mRNA in prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 13;18(6):e0286996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286996. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37310937 Free PMC article.
-
Human pancreatic islet microRNAs implicated in diabetes and related traits by large-scale genetic analysis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Feb 14;120(7):e2206797120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2206797120. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36757889 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA Deep Sequencing Identifies a Unique miRNA Signature Released in Serum Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Sjögren's Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 17;11:1475. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01475. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849505 Free PMC article.
-
These Are the Genes You're Looking For: Finding Host Resistance Genes.Trends Microbiol. 2021 Apr;29(4):346-362. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Trends Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33004258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFN-I inducible miR-3614-5p targets ADAR1 isoforms and fine tunes innate immune activation.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:939907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.939907. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35935998 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610. - PubMed
-
- O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Baltimore D. microRNA regulation of inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:295–312. - PubMed
-
- Vigorito E, Kohlhaas S, Lu D, Leyland R. miR-155: an ancient regulator of the immune system. Immunol Rev. 2013;253:146–157. - PubMed
-
- Mehta A, Baltimore D. MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:279–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

