Mitochondrial Sirtuin 3: New emerging biological function and therapeutic target
- PMID: 32724473
- PMCID: PMC7381741
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.45922
Mitochondrial Sirtuin 3: New emerging biological function and therapeutic target
Abstract
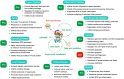
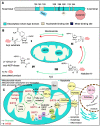
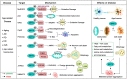
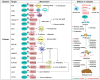
Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) is one of the most prominent deacetylases that can regulate acetylation levels in mitochondria, which are essential for eukaryotic life and inextricably linked to the metabolism of multiple organs. Hitherto, SIRT3 has been substantiated to be involved in almost all aspects of mitochondrial metabolism and homeostasis, protecting mitochondria from a variety of damage. Accumulating evidence has recently documented that SIRT3 is associated with many types of human diseases, including age-related diseases, cancer, heart disease and metabolic diseases, indicating that SIRT3 can be a potential therapeutic target. Here we focus on summarizing the intricate mechanisms of SIRT3 in human diseases, and recent notable advances in the field of small-molecule activators or inhibitors targeting SIRT3 as well as their potential therapeutic applications for future drug discovery.
Keywords: Age-related disease; Cancer; Mitochondrial homeostasis; SIRT3; SIRT3 activator; SIRT3 inhibitor.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Advances in characterization of SIRT3 deacetylation targets in mitochondrial function.Biochimie. 2020 Dec;179:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.08.021. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 32898647 Review.
-
Sirtuin 3: Emerging therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Feb 20;180:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.005. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35031448 Review.
-
Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3), a therapeutic target with oncogenic and tumor-suppressive function in cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Feb 6;5(2):e1047. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.14. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24503539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and aging diminish sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-mediated deacetylation of SIRT3, leading to hyperacetylation and decreased activity and stability of SIRT3.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 20;292(42):17312-17323. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778720. Epub 2017 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28808064 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 3 in renal diseases and aging: From mechanisms to potential therapies.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Aug;206:107261. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107261. Epub 2024 Jun 23. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38917912 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Protein Diet Inhibits the Synovial Tissue Macrophage Pro-Inflammatory Polarization Via NRF2/SIRT3/SOD2/ROS Pathway in K/BxN Rheumatoid Arthritis Mice.Inflammation. 2024 Sep 18. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02145-9. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39292325
-
Mammalian STE20-like kinase 1 inhibits synoviocytes activation in rheumatoid arthritis through mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by SIRT3/mTOR axis.Inflamm Res. 2024 Mar;73(3):415-432. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01846-5. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38265688
-
Increased Expression of Transferrin Receptor 1 in the Brain Cortex of 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease Is Associated with Activation of HIF-1 Signaling Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6383-6394. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03990-3. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38296900 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Chronic Degenerative Diseases: New Metabolic Targets in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3212. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063212. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircCCDC66: Emerging roles and potential clinical values in malignant tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 9;12:1061007. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1061007. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36698408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schwer B, Verdin E. Conserved metabolic regulatory functions of sirtuins. Cell Metab. 2008;7:104–12. - PubMed
-
- Frye RA. Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene: Sir2-like proteins (sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;260:273–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

