MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury
- PMID: 32717951
- PMCID: PMC7464779
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9081767
MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury
Abstract
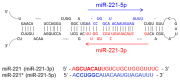
The last decade has witnessed significant advancements in our understanding of how small noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), regulate disease progression. One such miRNA, miR-221, has been shown to play a key role in the progression of liver fibrosis, a common feature of most liver diseases. Many reports have demonstrated the upregulation of miR-221 in liver fibrosis caused by multiple etiologies such as viral infections and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Inhibition of miR-221 via different strategies has shown promising results in terms of the suppression of fibrogenic gene signatures in vitro, as well as in vivo, in independent mouse models of liver fibrosis. In addition, miR-221 has also been suggested as a noninvasive serum biomarker for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. In this review, we discuss the biology of miR-221, its significance and use as a biomarker during progression of liver fibrosis, and finally, potential and robust approaches that can be utilized to suppress liver fibrosis via inhibition of miR-221.
Keywords: HCC; NASH; liver fibrosis; miR-221; noninvasive biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular regulation of miRNAs and potential biomarkers in the progression of hepatic steatosis to NASH.Biomark Med. 2015;9(11):1189-200. doi: 10.2217/bmm.15.70. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Biomark Med. 2015. PMID: 26506944 Review.
-
MicroRNA-21 is associated with fibrosis in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and serves as a plasma biomarker for fibrotic liver disease.Toxicol Lett. 2016 Sep 6;258:159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.06.012. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Toxicol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27320964
-
Circulating miRNAs associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Feb 1;324(2):C588-C602. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00253.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36645666 Review.
-
miR-21 ablation and obeticholic acid ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Apr 13;8(4):e2748. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.172. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28406477 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA signature in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma associated with type 2 diabetes.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov 14;25(42):6322-6341. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i42.6322. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31754293 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epidemiologic, Genetic, Pathogenic, Metabolic, Epigenetic Aspects Involved in NASH-HCC: Current Therapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 20;15(1):23. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010023. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum microRNA Profiles and Pathways in Hepatitis B-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A South African Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):975. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020975. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATF3 is involved in rSjP40-mediated inhibition of HSCs activation in Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18458. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18458. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39031798 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 23;24(19):14482. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914482. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum MicroRNAs as Predictors for HCV Progression and Response to Treatment in Pakistani Patients.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;14(2):441. doi: 10.3390/genes14020441. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833368 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

