The Role of Inflammation after Surgery for Elders (RISE) study: Examination of [11C]PBR28 binding and exploration of its link to post-operative delirium
- PMID: 32712451
- PMCID: PMC7390821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102346
The Role of Inflammation after Surgery for Elders (RISE) study: Examination of [11C]PBR28 binding and exploration of its link to post-operative delirium
Abstract
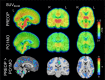
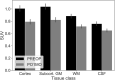
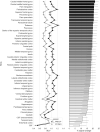
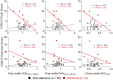
Major surgery is associated with a systemic inflammatory cascade that is thought, in some cases, to contribute to transient and/or sustained cognitive decline, possibly through neuroinflammatory mechanisms. However, the relationship between surgery, peripheral and central nervous system inflammation, and post-operative cognitive outcomes remains unclear in humans, primarily owing to limitations of in vivo biomarkers of neuroinflammation which vary in sensitivity, specificity, validity, and reliability. In the present study, [11C]PBR28 positron emission tomography, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and blood plasma biomarkers of inflammation were assessed pre-operatively and 1-month post-operatively in a cohort of patients (N = 36; 30 females; ≥70 years old) undergoing major orthopedic surgery under spinal anesthesia. Delirium incidence and severity were evaluated daily during hospitalization. Whole-brain voxel-wise and regions-of-interest analyses were performed to determine the magnitude and spatial extent of changes in [11C]PBR28 uptake following surgery. Results demonstrated that, compared with pre-operative baseline, [11C]PBR28 binding in the brain was globally downregulated at 1 month following major orthopedic surgery, possibly suggesting downregulation of the immune system of the brain. No significant relationship was identified between post-operative delirium and [11C]PBR28 binding, possibly due to a small number (n = 6) of delirium cases in the sample. Additionally, no significant relationships were identified between [11C]PBR28 binding and CSF/plasma biomarkers of inflammation. Collectively, these results contribute to the literature by demonstrating in a sizeable sample the effect of major surgery on neuroimmune activation and preliminary evidence identifying no apparent associations between [11C]PBR28 binding and fluid inflammatory markers or post-operative delirium.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Inflammation after Surgery for Elders (RISE) study: Study design, procedures, and cohort profile.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2019 Nov 6;11:752-762. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.09.004. eCollection 2019 Dec. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31737775 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid inflammation and the blood-brain barrier in older surgical patients: the Role of Inflammation after Surgery for Elders (RISE) study.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Apr 30;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02145-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33931093 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation activates microglia: [¹¹C]PBR28 positron emission tomography in nonhuman primates.Neuroimage. 2012 Oct 15;63(1):232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.055. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22776451 Free PMC article.
-
Increased in vivo glial activation in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: assessed with [(11)C]-PBR28.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Jan 19;7:409-14. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.01.009. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 25685708 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammatory challenges compromise neuronal function in the aging brain: Postoperative cognitive delirium and Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2017 Mar 30;322(Pt B):269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.08.027. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 27544872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural integrity of the anterior mid-cingulate cortex contributes to resilience to delirium in SuperAging.Brain Commun. 2022 Jun 28;4(4):fcac163. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac163. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 35822100 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pre-operative ibuprofen improves cognition in a rat model for postoperative cognitive dysfunction.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Jul 8;18(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02206-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34238316 Free PMC article.
-
Association between baseline serum bicarbonate and the risk of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing cardiac surgery in the ICU: a retrospective study from the MIMIC-IV database.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Sep 28;24(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02738-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39342157 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory and nutritional markers predict the risk of post-operative delirium in elderly patients following total hip arthroplasty.Front Nutr. 2023 Nov 2;10:1158851. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1158851. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38024358 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of delirium risk in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 May 12;15:1174644. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1174644. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37251808 Free PMC article. Review.

