Influence of reaming intramedullary nailing on MSC population after surgical treatment of patients with long bone fracture
- PMID: 32705190
- PMCID: PMC7411410
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11320
Influence of reaming intramedullary nailing on MSC population after surgical treatment of patients with long bone fracture
Abstract
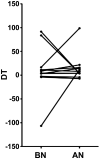
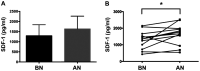
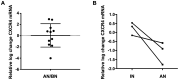
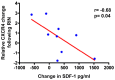
Reamed intramedullary nailing (RIN) is a surgical method of choice for treatment of diaphyseal fractures. This procedure affects the biological environment of bone tissue locally and systemically. This study investigated the influence of RIN on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in patients with long bone fractures. The axis of C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4)/stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF‑1) was selected since it is considered as major pathway for MSC homing and migration. Iliac crest bone marrow (IC‑BM) samples and blood samples were collected at two different time points. One sample was collected before the RIN (BN) and the other immediately after RIN (AN). BM‑MSCs were cultured and RT‑qPCR was performed for CXCR4 mRNA levels and ELISA for the SDF‑1 sera levels. The experimental study revealed that there was a correlation between the increase of SDF‑1 levels in peripheral blood and a decrease in the levels of CXCR4 in MSCs in the IC‑BM following RIN. The levels of SDF‑1 showed a significant increase in the sera of patients after RIN. In conclusion, the present study is the first providing evidence of the effects of RIN on MSC population via the CXCR4/SDF‑1 axis. The levels of serum SDF‑1 factor were elevated after RIN while increased levels of SDF‑1 in peripheral blood were inversely correlated with the mRNA levels of CXCR4 on BM‑MSCs after RIN. Therefore, this study contributes to enlighten the systematic effects of RIN on the population of MSCs at a cellular level.
Keywords: reaming intramedullary nailing; long bone fracture; mesenchymal stem cells; SdF-1; cXcr4.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the HIF‑1α/SDF‑1/CXCR4 signaling axis in accelerated fracture healing after craniocerebral injury.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Oct;22(4):2767-2774. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11361. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32945380 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing stromal cell- derived factor 1 aid in bone formation in osteoporotic mice.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 4;25(1):878. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07957-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39497150 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Platelet Aggregates Increased in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Might Depend on the Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1/CXCR4 Axis.Stem Cells Dev. 2019 Dec 15;28(24):1607-1619. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0154. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Stem Cells Dev. 2019. PMID: 31650891
-
The effect of reamed and nonreamed intramedullary nailing on fracture healing.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998 Oct;(355 Suppl):S230-8. doi: 10.1097/00003086-199810001-00023. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. PMID: 9917642 Review.
-
[Systemic complications in intramedullary nailing].Orthopade. 1996 Jun;25(3):292-9. Orthopade. 1996. PMID: 8766666 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Adipose tissue in bone regeneration - stem cell source and beyond.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Jun 26;14(6):372-392. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i6.372. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35949397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of a Minimally Invasive Traction Repositor versus Conventional Manual Traction for the Treatment of Tibial Fractures: A Comparative Study from a Tertiary Hospital in China.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Sep 23;18:945-954. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S379135. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 36176542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansen ST, Winquist RA. Closed intramedullary nailing of the femur. Küntscher technique with reaming. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;138:56–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

