Identification of long non-coding RNAs in advanced prostate cancer associated with androgen receptor splicing factors
- PMID: 32704143
- PMCID: PMC7378231
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01120-y
Identification of long non-coding RNAs in advanced prostate cancer associated with androgen receptor splicing factors
Abstract
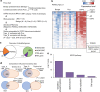
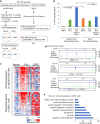
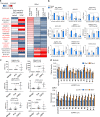
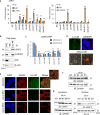
The molecular and cellular mechanisms of development of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) remain elusive. Here, we analyzed the comprehensive and unbiased expression profiles of both protein-coding and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) using RNA-sequencing to reveal the clinically relevant molecular signatures in CRPC tissues. For protein-coding genes upregulated in CRPC, we found that mitochondria-associated pathway, androgen receptor (AR), and spliceosome associated genes were enriched. Moreover, we discovered AR-regulated lncRNAs, CRPC-Lncs, that are highly expressed in CRPC tissues. Notably, silencing of two lncRNAs (CRPC-Lnc #6: PRKAG2-AS1 and #9: HOXC-AS1) alleviated CRPC tumor growth, showing repression of AR and AR variant expression. Mechanistically, subcellular localization of the splicing factor, U2AF2, with an essential role in AR splicing machinery was modulated dependent on the expression level of CRPC-Lnc #6. Thus, our investigation highlights a cluster of lncRNAs which could serve as AR regulators as well as potential biomarkers in CRPC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vav3 enhances androgen receptor splice variant activity and is critical for castration-resistant prostate cancer growth and survival.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Dec;26(12):1967-79. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1165. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 23023561 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00675 activates androgen receptor axis signaling pathway to promote castration-resistant prostate cancer progression.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 15;11(8):638. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02856-5. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32801300 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Inhibits Androgen Receptor Splice Variant-7 (AR-V7)-Induced Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Activation and NF-κB Activator-Induced AR-V7 Expression in Prostate Cancer Cells: Potential Implications for the Use of Melatonin in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 31;18(6):1130. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061130. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28561752 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing Factors Have an Essential Role in Prostate Cancer Progression and Androgen Receptor Signaling.Biomolecules. 2019 Apr 1;9(4):131. doi: 10.3390/biom9040131. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30939845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgen receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms driving prostate cancer progression: Opportunities for therapeutic targeting from multiple angles.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3724-3745. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12554. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27741508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of DNA damage response-related genes as biomarkers for castration-resistant prostate cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 10;13(1):19602. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46651-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37950047 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Mitochondrial-Related Genes NDUFA10 and NDUFV2 as Prognostic Markers for Prostate Cancer through Biclustering.Biomed Res Int. 2021 May 22;2021:5512624. doi: 10.1155/2021/5512624. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34124242 Free PMC article.
-
A TGF-β signaling-related lncRNA signature for prediction of glioma prognosis, immune microenvironment, and immunotherapy response.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14489. doi: 10.1111/cns.14489. Epub 2023 Oct 18. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37850692 Free PMC article.
-
Long-range gene regulation in hormone-dependent cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2023 Oct;23(10):657-672. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00603-4. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37537310 Review.
-
Targeting phase separation on enhancers induced by transcription factor complex formations as a new strategy for treating drug-resistant cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 3;12:1024600. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1024600. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36263200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

